When it comes to understanding early head and neck cancer symptoms, it’s essential to be vigilant. Head and neck cancer can affect various areas in the head and neck region, including the mouth, throat, nose, sinuses, and salivary glands. Detecting these cancers in their early stages is crucial for successful treatment and a better prognosis. In this blog post, we will explore the early head and neck cancer symptoms, helping you understand what to look out for and when to seek medical attention.
Top 7 Early Head and Neck Cancer Symptoms
Persistent Sore Throat or Hoarseness
A persistent sore throat or hoarseness is one of the classic early head and neck cancer symptoms. It’s easy to dismiss a sore throat as a minor irritation, especially during cold and flu seasons. However, when this discomfort lingers for an extended period, it’s a cause for concern.
The reason why a lingering sore throat or hoarseness should raise red flags is that it can be indicative of something more serious going on within the throat or neck. Healthy throats usually recover within a week or two after irritation from a viral infection or excessive voice strain. But if your sore throat persists for several weeks without improvement, it’s time to take action.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can be an alarming symptom of head and neck cancer. If you experience pain or discomfort while swallowing food or liquids, or if you notice that it feels like something is blocking your throat, don’t ignore it. These early head and neck cancer symptoms should be evaluated by a doctor.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Early head and neck cancer symptoms can manifest in unexpected ways, and one such subtle yet concerning sign is unexplained weight loss. Let’s delve into why this symptom is a potential indicator of head and neck cancer and why seeking medical attention promptly is imperative.
Swelling or Lump in the Neck
In the realm of early head and neck cancer symptoms, the presence of a swelling or lump in the neck can be particularly alarming. This symptom warrants careful consideration and immediate medical assessment.
Changes in Voice
If your voice undergoes noticeable changes, such as becoming hoarse or having a different quality, and these changes persist for more than a few weeks, it’s essential to consult a doctor. Changes in voice can be indicative of throat or vocal cord issues, which may be linked to head and neck cancer.
Persistent Ear Pain
Ear pain, particularly when it occurs on one side and is not associated with an ear infection or other obvious causes, can be a symptom of head and neck cancer. The pain may radiate from the throat or mouth area, making it crucial to investigate its underlying cause.
Oral Symptoms
Oral symptoms can be early indicators of head and neck cancer. These may include:
- Red or white patches in the mouth
- Persistent mouth ulcers
- Difficulty moving the tongue or jaw
- Changes in the fit of dentures
If you notice any of these oral symptoms that do not resolve within a reasonable time, it’s crucial to consult a dentist or oral health specialist.
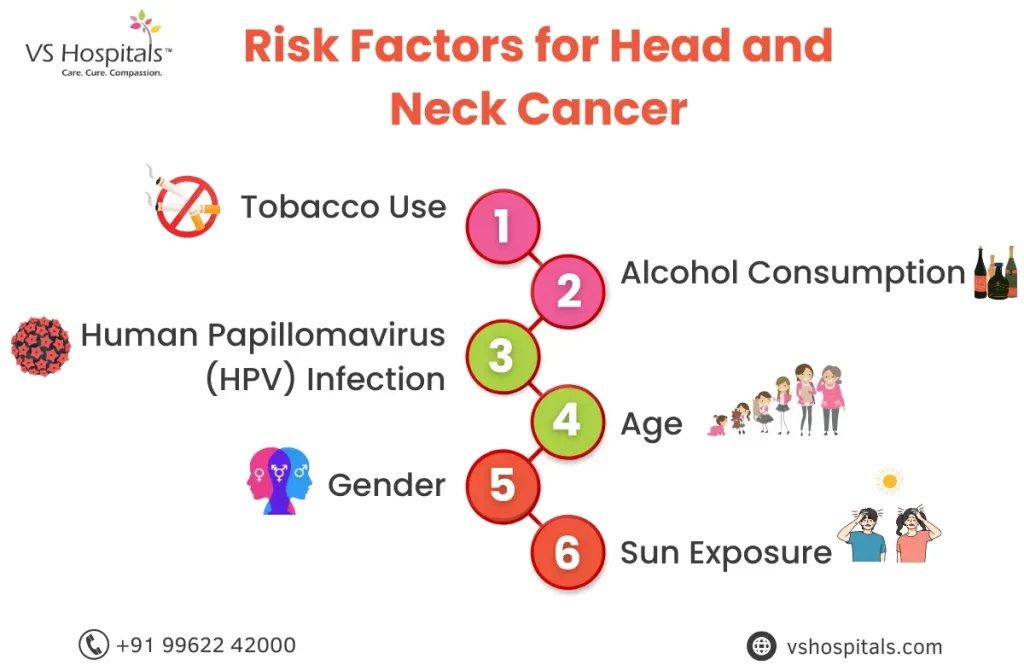
Risk Factors for Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer can be influenced by various risk factors, some of which are modifiable, while others are beyond an individual’s control. Here are the key risk factors for head and neck cancer:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and using smokeless tobacco products significantly increases the risk of head and neck cancer. The risk is higher for long-term and heavy tobacco users.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive and long-term alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for head and neck cancer, especially when combined with tobacco use. Alcohol can irritate the lining of the mouth and throat, making it more susceptible to cancer.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16 and HPV-18, are associated with an increased risk of oropharyngeal cancers, especially in the tonsils and base of the tongue. HPV-related head and neck cancers are becoming more common, particularly among younger individuals.
- Age: The risk of head and neck cancer increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in people over 50.
- Gender: Men are at a higher risk of developing head and neck cancer than women, although the gap is narrowing due to changing patterns of tobacco and alcohol use.
- Sun Exposure: Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, especially on the lips, can increase the risk of lip cancer.
Conclusion
Recognizing early head and neck cancer symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment. If you or someone you know experiences any of the symptoms mentioned above, seek medical advice promptly. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers and dentists can also help in the early detection of head and neck cancer, ensuring better outcomes for those at risk.
Read also Signs and Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer.