Esophageal cancer is a serious condition that affects the tube connecting your throat to your stomach, known as the esophagus. Like most cancers, early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes. Being aware of the early symptoms of esophageal cancer can help you seek medical attention promptly and improve your chances of a positive prognosis. In this blog, we’ll discuss the key indicators that could signal the presence of esophageal cancer.
Early Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
One of the most common early symptoms of esophageal cancer is difficulty swallowing, medically termed dysphagia. If you find it challenging to swallow solid foods or even liquids, and this problem persists over time, it could be a red flag. This occurs because the growing tumor narrows the esophagus, making it harder for food and fluids to pass through.
Unintended Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying might seem like a positive outcome, but when it happens without changes to your diet or exercise routine, it could be indicative of a health issue, including early symptoms of esophageal cancer. As the cancer progresses, it can lead to a decrease in appetite and difficulty in consuming enough calories, resulting in weight loss. This unintentional weight loss is often a warning sign that shouldn’t be overlooked, as it can provide valuable insights into your overall health.
Persistent Indigestion or Heartburn
Frequent indigestion, acid reflux, or heartburn that doesn’t respond well to typical over-the-counter medications could be a warning sign of early symptoms of esophageal cancer. While occasional heartburn is normal, chronic or worsening symptoms might suggest something more serious, including the possibility of esophageal cancer. It’s important to pay attention to your body and recognize when something doesn’t feel right.
Pain or Discomfort
Persistent pain or discomfort in the chest, throat, or back could be another early indication of esophageal cancer. This discomfort might be experienced while swallowing or at other times, and it’s essential not to dismiss such symptoms as they could be linked to the presence of a tumor.
Chronic Cough or Hoarseness
If you have a chronic cough or experience hoarseness that lingers for an extended period, it might be worth investigating further. The cancerous growth can sometimes affect the nerves and tissues around the esophagus, leading to such symptoms.
Regurgitation or Vomiting Blood
Regurgitating food, experiencing bloody vomit, or noticing blood in your stools can be alarming signs. These symptoms might indicate that the tumor has reached an advanced stage and is causing internal bleeding.
Chronic Hiccups
Although less common, persistent and unexplained hiccups could also be an early symptom of esophageal cancer. The irritation caused by the tumor could affect the diaphragm and trigger recurrent hiccups. While hiccups are typically harmless and temporary, chronic hiccups that persist for an extended period, especially when combined with other potential indicators of esophageal cancer, should not be overlooked.
Unusual Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
- Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that doesn’t seem to go away might be indicative of esophageal cancer. Cancerous cells can stimulate the nerves in the chest, leading to a chronic cough.
- Hoarseness or Voice Changes: Unusual changes in voice, such as persistent hoarseness, can result from the tumor affecting the nerves that control the vocal cords.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some individuals might experience pain or discomfort behind the breastbone or in the back. This discomfort could range from mild to severe and might be present even when swallowing is not occurring.
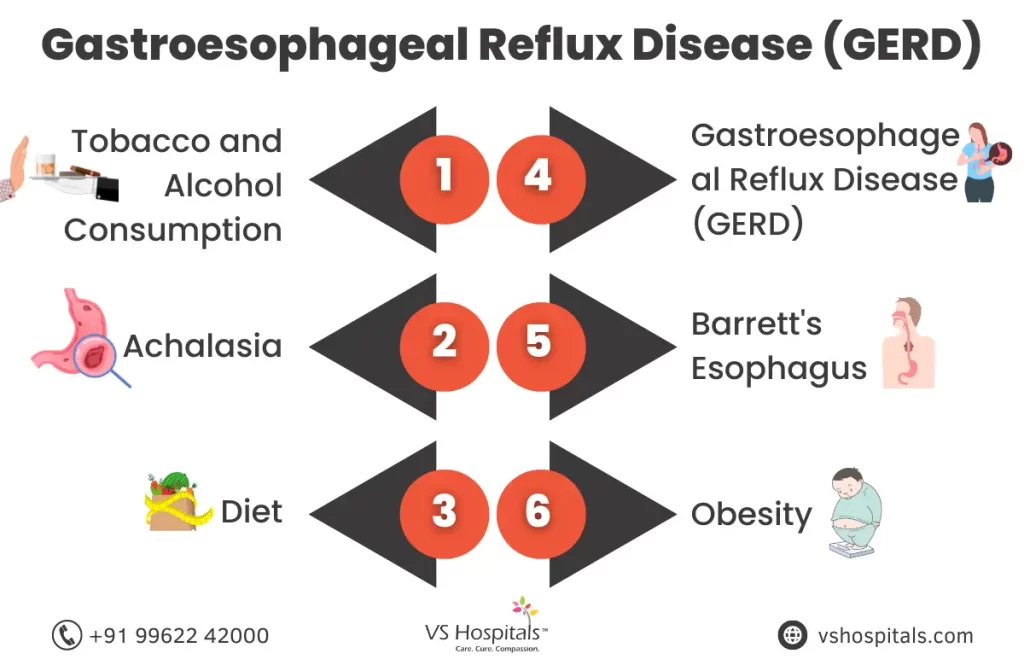
Causes of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer typically develops over time due to a combination of factors. The primary risk factors for these types include:
- Chronic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Persistent acid reflux can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a condition that increases the risk of adenocarcinoma.
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can significantly elevate the risk of esophageal cancer, especially squamous cell carcinoma.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the likelihood of developing adenocarcinoma, possibly due to increased pressure on the stomach and chronic inflammation.
- Poor Diet: Diets low in fruits and vegetables might contribute to an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
Conclusion
Esophageal cancer, like any cancer, is best treated when detected early. Being vigilant about your health and recognizing the early symptoms of esophageal cancer can facilitate prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention. If you notice any of the mentioned signs, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Remember, your well-being is a priority, and early action can make a significant difference in your journey toward recovery.
Read also How to Check Breast Cancer at Home.
