Advanced X-Ray Services | Accurate Diagnostic
Get advanced X-Ray services with high-quality imaging and expert radiologists for accurate diagnosis, quick results, and effective treatment planning.
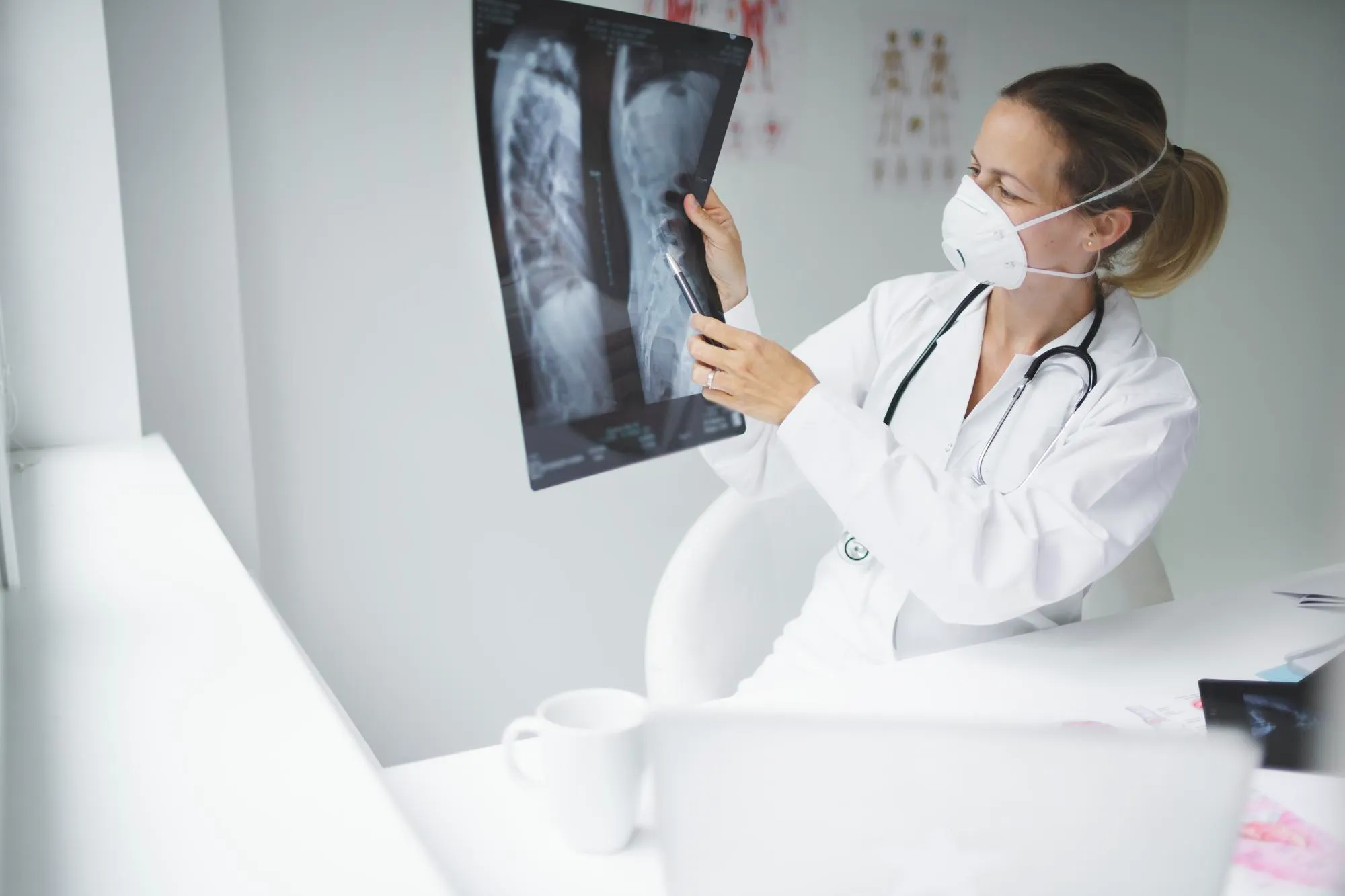
X-Ray
An X-ray is one of the most common and essential medical imaging tests used to view the internal structures of the body. It helps doctors detect fractures, infections, lung conditions, and even dental issues. The process is fast, painless, and highly effective in diagnosing health problems without surgery. Using small amounts of radiation, X-rays capture detailed images of bones and tissues, allowing healthcare professionals to make quick and accurate clinical decisions. It’s a cornerstone of modern diagnostics used in hospitals, dental clinics, and emergency rooms worldwide.
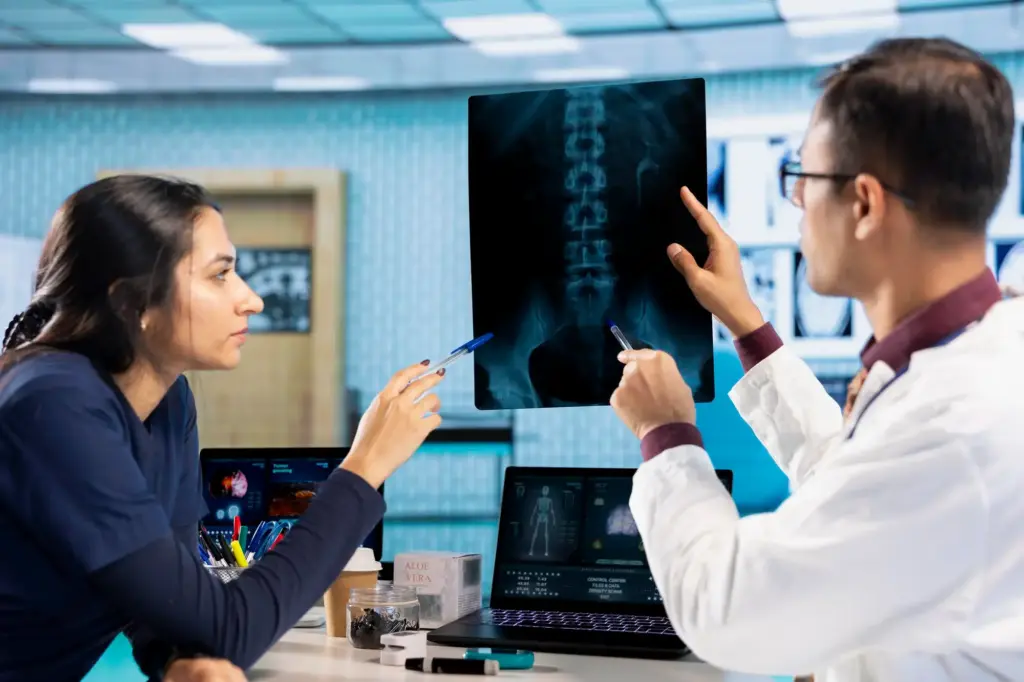

100 million
100 million x-rays are taken annually in India
0.01 nm to 10 nm
Diagnostic x-rays don’t increase the risk of cancer and it usually lie in the range of 0.01 nm to 10 nm (nanometres)
10,000
There are around 10,000 trained radiologists for the current population all over India
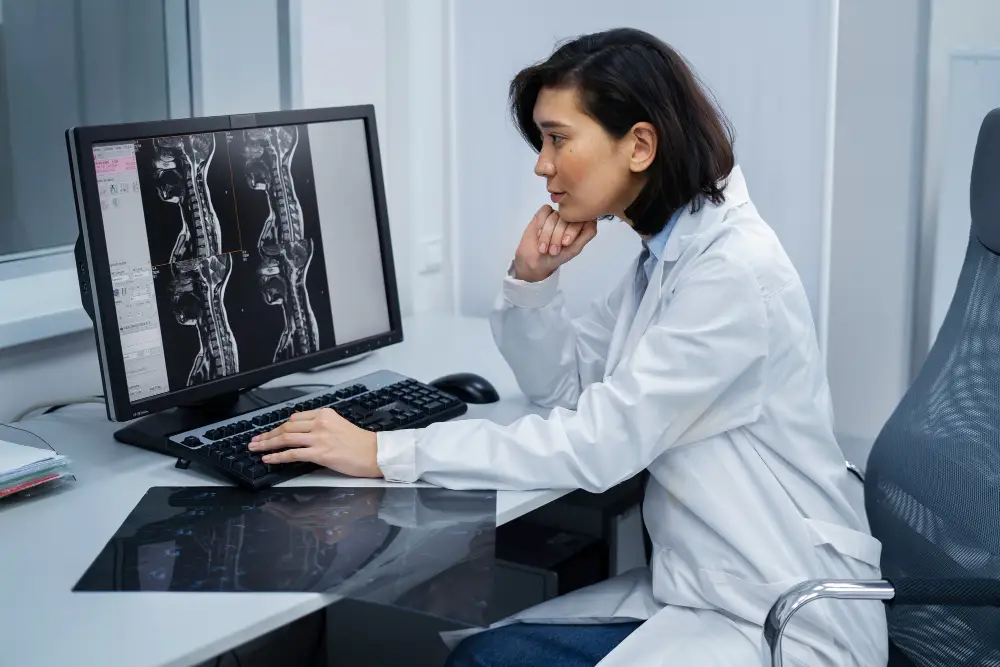

How X-Ray Works
The science behind an X-ray is simple yet fascinating. It uses electromagnetic radiation that passes through the body to create images on a special detector or film. Different tissues absorb radiation differently — bones, being dense, appear white; softer tissues appear gray; and air-filled spaces, like the lungs, appear black. A machine directs a focused X-ray beam toward the target area while a detector captures the resulting image. Advanced digital X-rays now provide sharper images instantly, reducing exposure and improving diagnostic accuracy.
Why X-Ray is Done
Bone and Joint Problems
Detecting fractures, dislocations, arthritis, or bone infections.
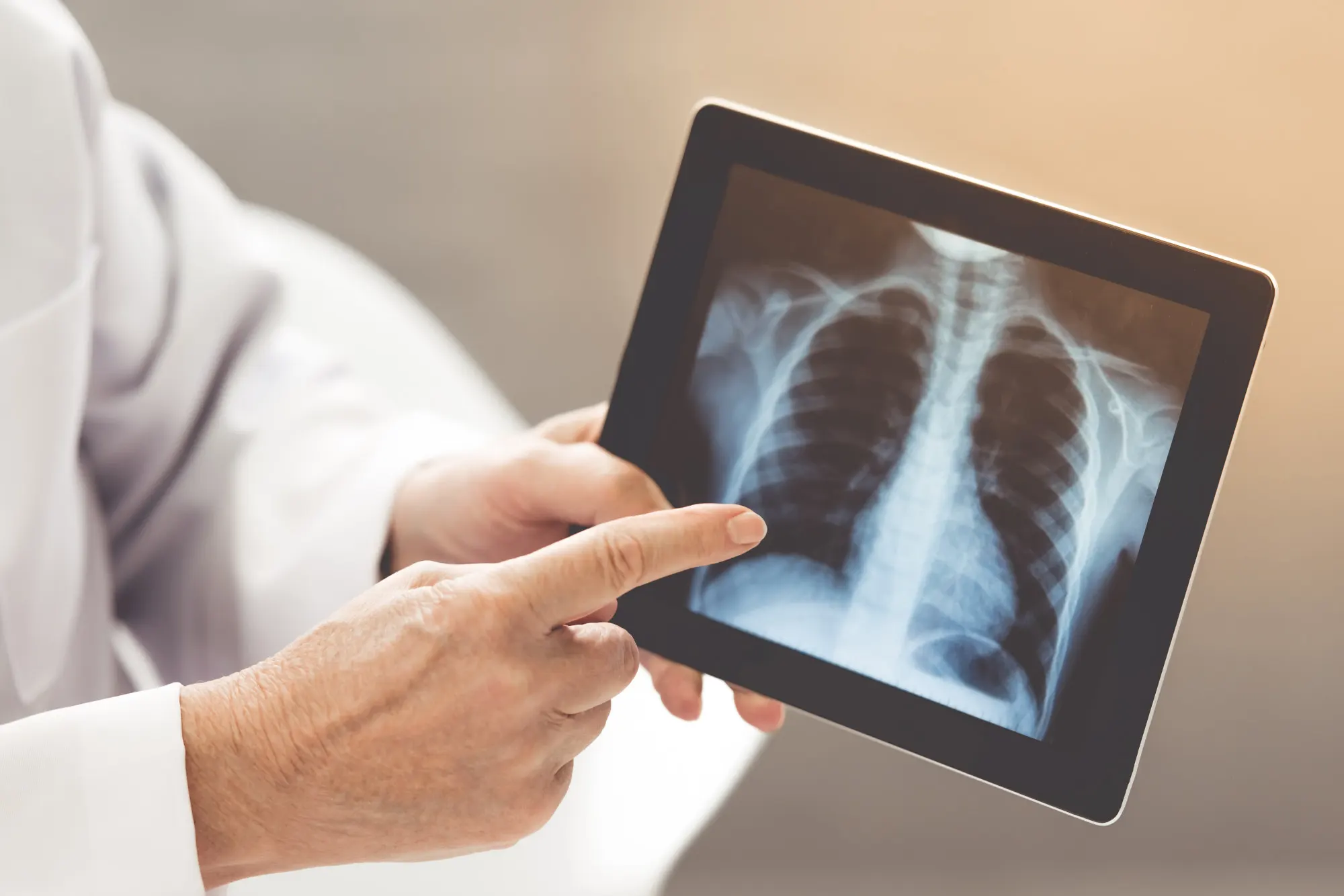
Chest and Lungs
Identifying pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer, or fluid accumulation.
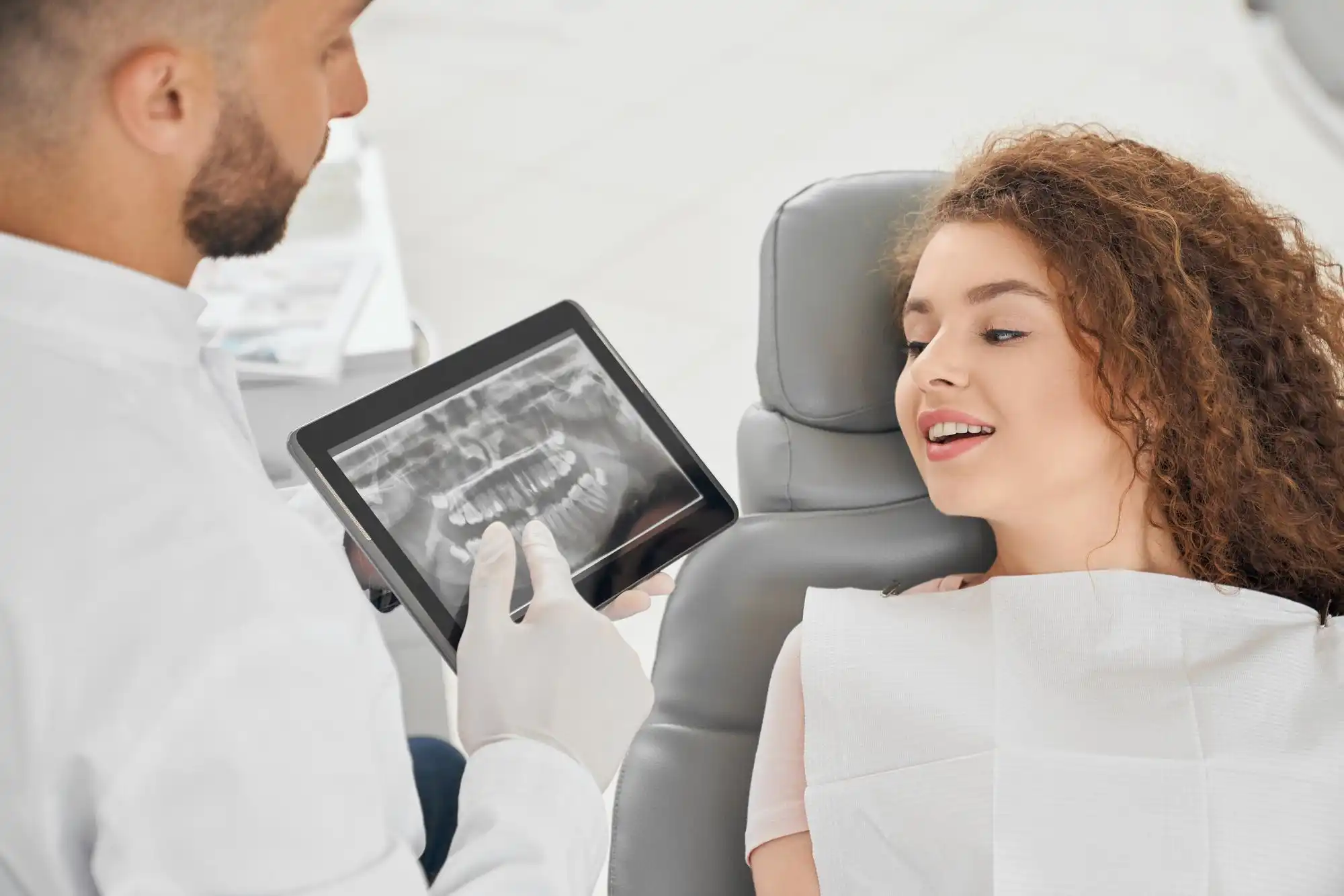
Dental Evaluation
Checking for cavities, tooth decay, or jawbone alignment.
Abdominal Issues
Spotting intestinal blockages, kidney stones, or swallowed objects.
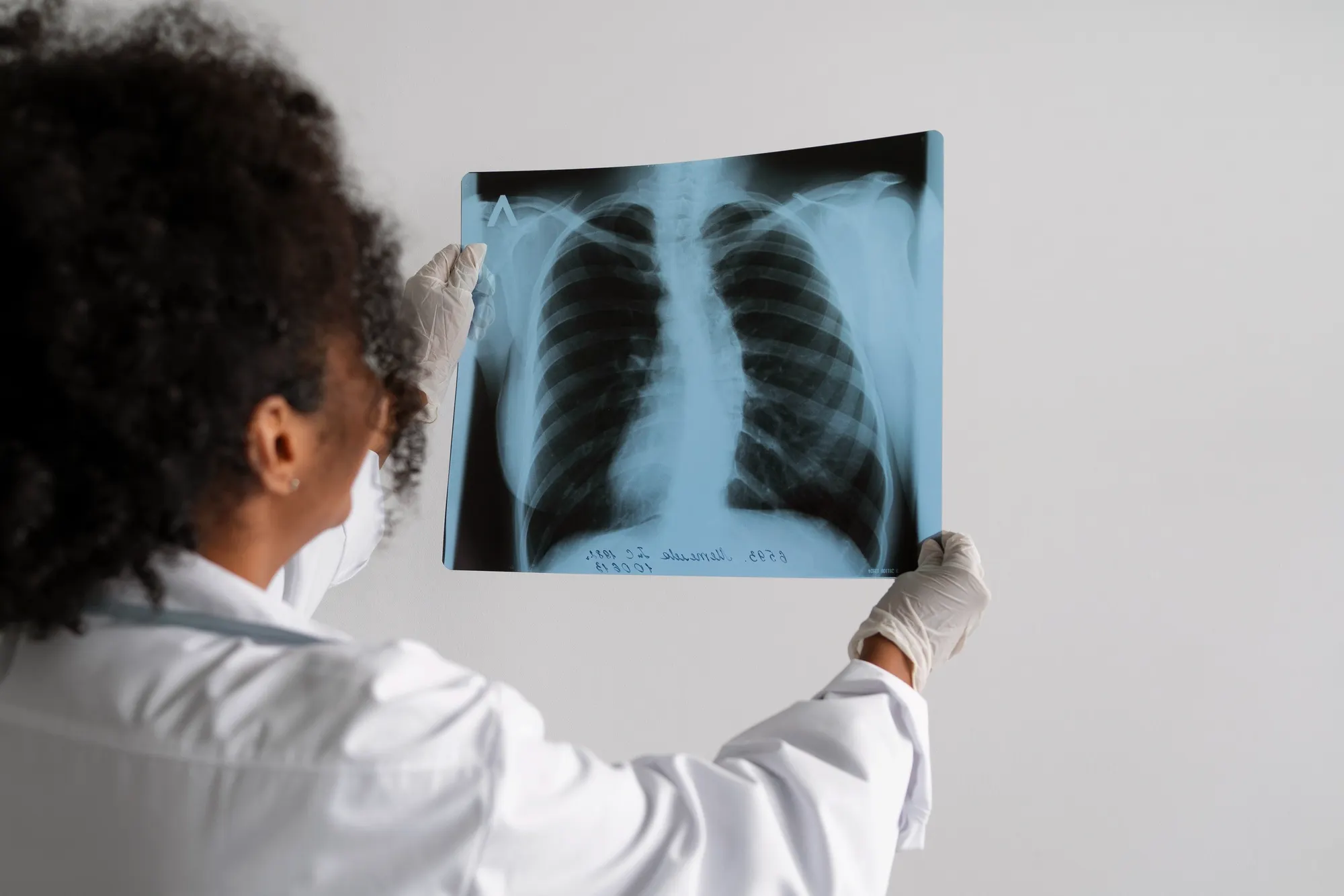
Heart and Blood Vessels
Using chest X-rays to detect enlarged hearts or vascular abnormalities.
Benefits of X-Ray
Quick and Accurate
Results are often available within minutes, aiding faster diagnosis.

Non-Invasive
No cuts, injections, or anesthesia just a simple scan.

Cost-Effective
Among the most affordable diagnostic imaging methods available.

Wide Application
Useful in orthopedics, cardiology, dentistry, pulmonology, and emergency care.
Early Detection
Helps identify diseases before symptoms become severe.

Digital Clarity
Modern X-rays offer enhanced precision and easy image storage for long-term monitoring.

Preparation Before an X-Ray
Preparation depends on the type and area being scanned:
- Clothing: Patients may need to change into a hospital gown and remove jewelry or metal objects that could interfere with imaging.
- Food and Drink: For some abdominal or digestive X-rays, fasting for a few hours may be necessary.
- Pregnancy: Women who are pregnant or suspect they might be should inform the technician, as precautions are taken to avoid unnecessary exposure.
- Contrast Use: In certain cases, a contrast dye may be used to highlight specific organs or blood vessels.
Most X-rays, however, require minimal preparation a huge reason for their popularity in emergency diagnostics.
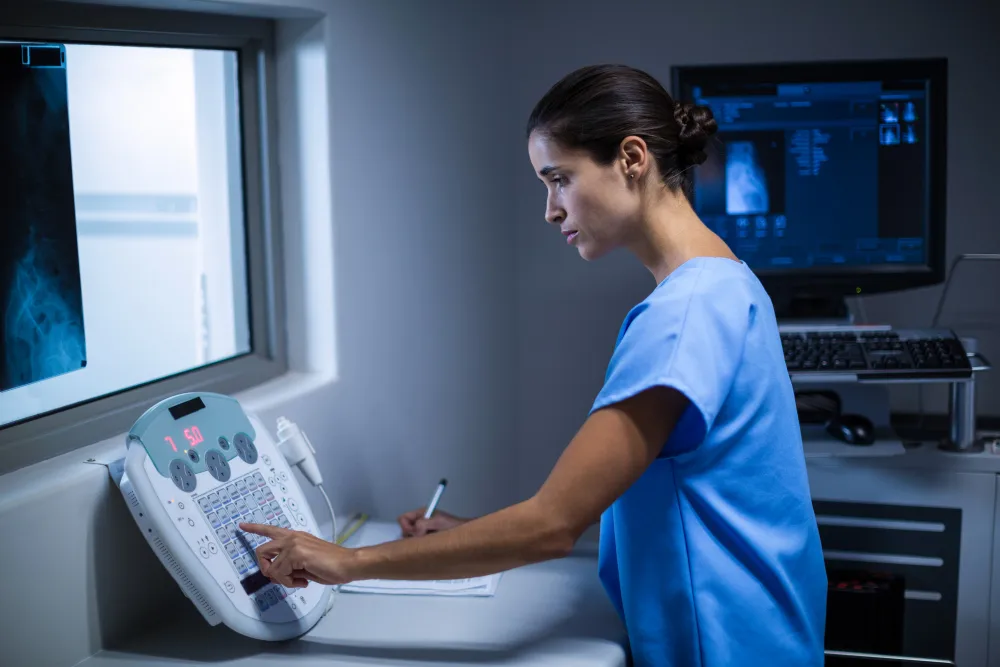

During the Procedure
The procedure is straightforward and typically lasts only a few minutes:
- You’ll be positioned either standing, sitting, or lying down based on the area being examined.
- A radiologic technologist will adjust the X-ray machine to focus on the specific region.
- You must remain still while the image is captured to avoid blurriness.
- Protective shields may be placed over parts of your body to minimize radiation exposure.
Some X-rays might require different angles or repeated scans for better accuracy. The process is painless, though holding still for a few seconds may feel slightly uncomfortable.
After the Procedure
Once the X-ray is done, there’s no recovery time required. You can return to your normal activities immediately. If a contrast dye was used, you might be asked to drink plenty of water to flush it from your system. A radiologist will review the images and send a detailed report to your doctor, who will discuss the findings and possible next steps, such as further scans or treatment.

