Ovarian cyst cancer treatment is a journey that begins with understanding ovarian cysts and how they can sometimes lead to cancer. By exploring the types, symptoms, causes, and stages of ovarian cancer, along with various treatment options, individuals gain essential knowledge to make informed decisions about their health. This guide empowers you with valuable information, helping you navigate the path to recovery and choose effective options for ovarian cyst cancer treatment with confidence.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the ovary begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a mass or tumor. While not all ovarian cysts are cancerous, certain types may develop into cancer, making “ovarian cyst cancer treatment” essential for those at risk. The ovaries are responsible for hormone production and egg release, so cancer in this area can affect multiple body systems. Early detection and understanding the nature of ovarian cancer are crucial in developing an effective, personalized treatment plan to manage or eliminate the disease.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
Understanding the various types of ovarian cancer is crucial for determining the most effective ovarian cyst cancer treatment. The primary categories include:
- Epithelial Tumors: These originate from the cells covering the ovary’s surface and are the most prevalent form.
- Stromal Tumors: Developing in the hormone-producing cells within the ovary, these tumors are less common.
- Germ Cell Tumors: Arising from the egg-producing cells, these rare tumors typically affect younger women.
Each type presents unique characteristics and may require different treatment approaches. Consulting with the best doctor for ovarian cysts is essential to determine the appropriate treatment plan tailored to the specific type of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Recognizing symptoms early is crucial in the effective management and timely ovarian cyst cancer treatment. Symptoms of ovarian cancer can be subtle and may often resemble common digestive or menstrual issues, leading to potential ways to remove ovarian cyst in diagnosis. However, being aware of these signs can be lifesaving. Key symptoms include:
- Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling
- Pain in the pelvic or lower abdominal area
- Feeling full quickly or loss of appetite
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a specialist promptly is vital. Early intervention enhances treatment options, improving the chances of successful ovarian cyst cancer treatment.
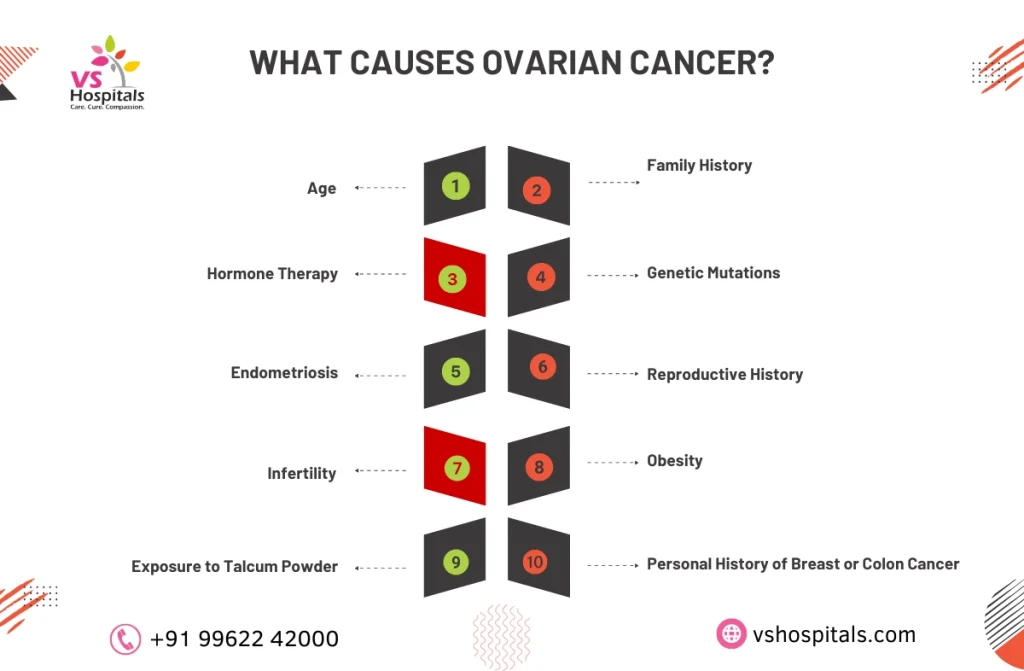
What Causes Ovarian Cancer?
The exact cause of ovarian cancer remains uncertain, but researchers have identified several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Understanding these causes is essential in preventing and planning effective ovarian cyst cancer treatment. Some of the known risk factors include:
- Family History: Women with close relatives who have had ovarian or breast cancer may have a higher risk.
- Age: Most cases of ovarian cancer occur in women over 50.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain inherited genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase ovarian cancer risk.
- Hormone Therapy: Postmenopausal hormone therapy may elevate risk.
Awareness of these factors can aid early detection and better outcomes in ovarian cyst cancer treatment.
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ways to remove ovarian cyst involves several steps to ensure accurate detection and effective treatment. Initially, a pelvic exam is conducted to check for abnormalities in the ovaries and surrounding areas. If concerns arise, further evaluations may include:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): Utilizes sound waves to create images of the ovaries, helping identify masses or cysts.
- CA-125 Blood Test: Measures the level of CA-125 protein, which can be elevated in ovarian cancer cases.
- Biopsy: Involves removing a tissue sample for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
These diagnostic tools are crucial in developing an effective ovarian cyst cancer treatment plan.
What are the Stages of Ovarian Cancer?
Understanding the stages of ovarian cancer is crucial for determining the most effective ovarian cyst cancer treatment. The stages are classified as follows:
- Stage 1: Cancer is confined to one or both ovaries.
- Stage 2: Cancer has spread to other pelvic organs.
- Stage 3: Cancer has extended to the abdominal lining or lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: Cancer has metastasized to distant organs, such as the liver or lungs.
Accurate staging is essential, as it guides the selection of appropriate ovarian cyst cancer treatments and helps predict patient outcomes.
Ovarian Cancer Treatment Options
When considering ovarian cyst cancer treatment, it’s essential to understand the various options available. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual’s specific condition and may include:
- Surgery: Often the first step, involving the removal of one or both ovaries, and sometimes surrounding tissues, to eliminate cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy: Utilizes drugs to destroy cancer cells, typically administered after surgery to target any remaining malignant cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Employs high-energy beams to kill cancer cells, though it’s less commonly used for ovarian cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic changes in cancer cells, aiming to inhibit their growth.
- Hormone Therapy: Slows the growth of certain ovarian cancers by blocking hormones that fuel cancer cell proliferation.
Consulting with the best doctor for ovarian cyst treatment is crucial to determine the most effective approach for your situation.
Conclusion
Ovarian cyst cancer treatment is a journey of resilience, knowledge, and partnership with trusted medical professionals. At VS Hospitals, we offer advanced treatment options, compassionate care, and specialized support at every step. If you’re experiencing symptoms or have been diagnosed, reaching out to our team ensures that you receive the guidance and treatment suited to your needs. Together, we can work towards effective recovery and renewed health, providing hope for a brighter, healthier future.
Read also Inflammatory breast cancer
