Menstrual Cycle Problems can be challenging, but with the right information and support, they’re manageable. Understanding different types of menstrual problems, their symptoms, and potential side effects empowers women to take control of their health. By addressing these issues early and seeking guidance when needed, you can improve your well-being. If you experience ongoing menstrual cycle problems, don’t hesitate to reach out to the experts at VS Hospitals for personalized care and effective treatment options tailored to your needs.
What Are Menstrual Cycle Problems?
Menstrual Cycle Problems refer to any issues or disruptions in the monthly menstrual cycle, which can affect both physical and emotional well-being. These problems can vary widely, from irregular or missed periods to intense pain or heavy bleeding, and each can have unique causes. For example, some women may experience stomach issues during their period, severe cramps, or side effects of irregular periods on the body, such as hormonal imbalances, fatigue, or mood changes. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding what’s normal versus problematic can help individuals manage these issues more effectively and know when it’s time to seek medical guidance.
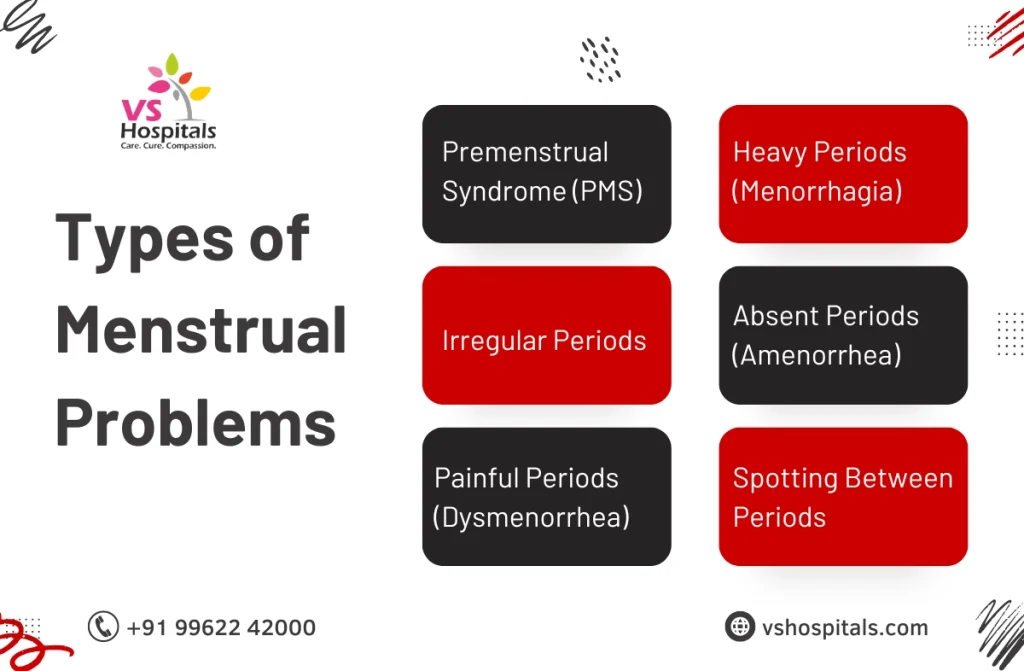
Types of Menstrual Problems
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
PMS affects many women before menstruation begins, causing mood swings, bloating, headaches, and stomach issues during periods. Physical symptoms like fatigue and breast tenderness are also common. PMS can vary in severity, affecting day-to-day activities and relationships. For some, it’s manageable with lifestyle changes, while others may need medical help to ease symptoms. Understanding PMS helps women identify triggers and find ways to feel better through a healthy diet, exercise, and stress management.
Heavy Periods (Menorrhagia)
Menorrhagia refers to abnormally heavy bleeding, often lasting longer than seven days. Women with heavy periods may need to change pads or tampons frequently and might experience fatigue due to blood loss. This condition can impact daily routines, leading to discomfort and even anemia in severe cases. Heavy periods can be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, or other underlying issues. Treatment options range from medication to lifestyle changes and, in some cases, surgical procedures.
Absent Periods (Amenorrhea)
Amenorrhea occurs when a woman misses her period for an extended period without pregnancy or menopause being the cause. Primary amenorrhea refers to never having menstruated, while secondary amenorrhea happens when regular periods suddenly stop. Causes include stress, excessive exercise, hormonal imbalances, or reproductive health issues. Amenorrhea may affect fertility and overall health, making it essential to identify the root cause. Treatment can involve lifestyle adjustments, addressing health issues, or hormone therapy as needed.
Painful Periods (Dysmenorrhea)
Dysmenorrhea describes intense menstrual cramps that can disrupt daily activities. Pain may occur in the lower abdomen, back, or thighs and is often accompanied by nausea, fatigue, or headaches. Primary dysmenorrhea is linked to normal menstrual processes, while secondary dysmenorrhea may stem from conditions like endometriosis or fibroids. Managing dysmenorrhea may include heat therapy, pain relievers, lifestyle changes, or medical interventions to address underlying causes. Many find relief through personalized treatment plans from healthcare providers.
Diagnosing Menstrual Problems
Diagnosing menstrual problems involves a comprehensive approach to identify the underlying causes of irregularities in the menstrual cycle. Healthcare providers typically follow these steps:
- Symptom Tracking: Keeping a detailed record of menstrual patterns, including cycle length, flow intensity, and associated symptoms like stomach issues during periods.
- Medical History Review: Discussing personal and family medical histories to identify potential genetic or lifestyle factors affecting the menstrual cycle.
- Physical Examination: Conducting a thorough pelvic exam to detect any abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
- Diagnostic Tests: Utilizing blood tests to assess hormone levels and imaging studies, such as ultrasounds, to examine the uterus and ovaries.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of menstrual cycle problems, helping to prevent side effects of irregular periods on the body.
Side Effects of Irregular Periods on the Body
Irregular periods can lead to various side effects on the body, affecting both physical and mental health. Understanding these impacts is crucial for managing and addressing menstrual cycle problems effectively.
Physical Effects:
- Fatigue: Inconsistent menstrual cycles can cause hormonal imbalances, leading to persistent tiredness.
- Skin Issues: Hormonal fluctuations may result in acne or other skin problems.
- Weight Changes: Some women experience unexplained weight gain or loss due to irregular periods.
Mental Health Effects:
- Mood Swings: Hormonal imbalances can cause emotional instability, including irritability and depression.
- Stress and Anxiety: Unpredictable cycles may lead to increased stress levels and anxiety.
Recognizing these side effects is the first step toward seeking appropriate treatment and improving overall well-being.
Treatment for Menstrual Disorders
Managing menstrual cycle problems involves various approaches tailored to individual needs. Common treatments include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing stress-reduction techniques can alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can ease cramps. Hormonal therapies, like birth control pills, may regulate cycles and reduce heavy bleeding.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, procedures like endometrial ablation or hysterectomy might be considered.
Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to determine the most effective treatment plan for your specific menstrual cycle problems.
Conclusion
Menstrual Cycle Problems can impact daily life, but they are manageable with the right approach. By understanding different types of menstrual problems, their symptoms, and the possible side effects on the body, women can take proactive steps toward better health. Addressing these concerns early and seeking expert help when needed can greatly improve quality of life. If you’re facing menstrual cycle problems, VS Hospitals offers personalized care and solutions to support your well-being and restore balance to your health.
Read also Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment
