PCL Injuries | Advanced Care & Recovery
Get expert care for PCL injuries with advanced diagnosis, minimally invasive treatments, and personalized rehab for fast and safe recovery.
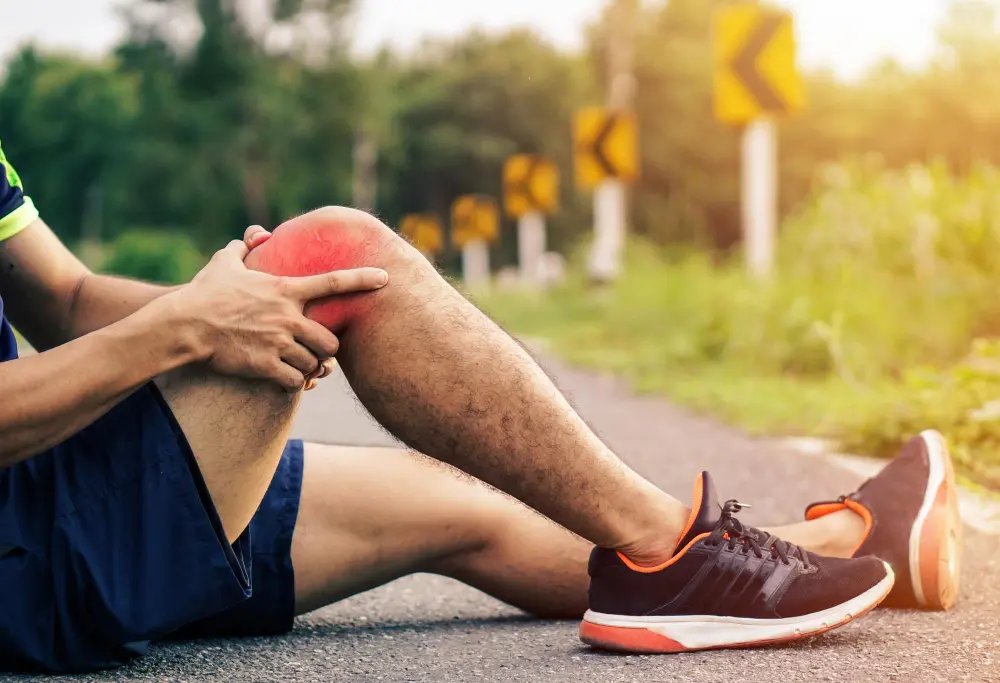

PCL Injuries
A PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament) injury occurs when the ligament, which stabilizes the knee joint, is torn or stretched. The PCL is one of the four major ligaments in the knee and is responsible for preventing the tibia (shin bone) from sliding backward relative to the femur (thigh bone). Though less common than ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injuries, PCL injuries can still lead to pain, instability, and long-term joint damage if left untreated.
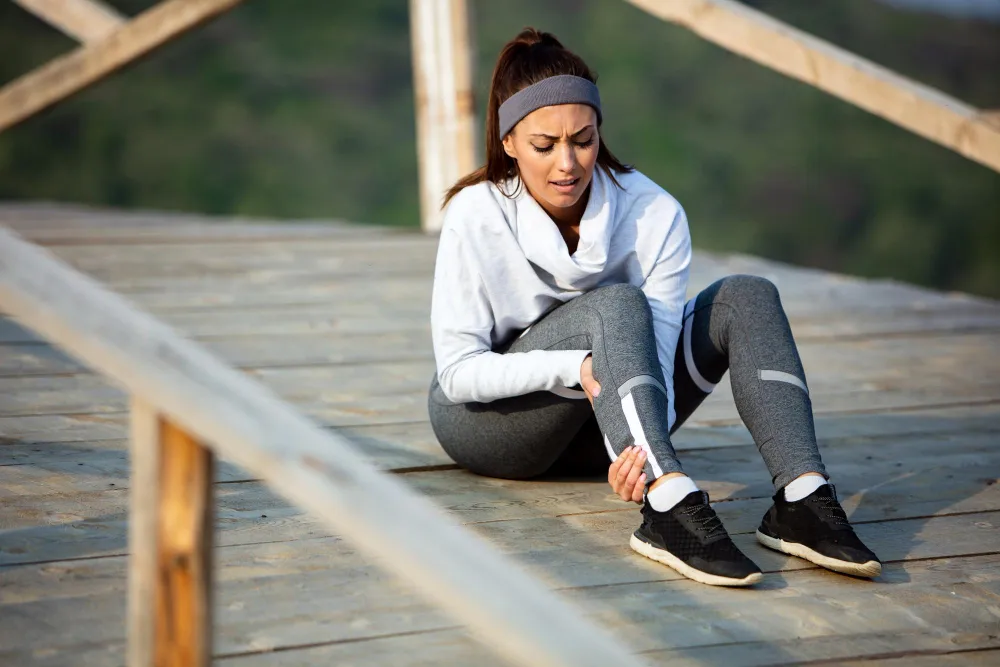

Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Pain in the Knee
The primary symptom is pain in the back of the knee, which can worsen with activity, especially during bending, jumping, or running.
Swelling
Swelling often occurs within a few hours of the injury, particularly if there is a tear or significant damage to the ligament.
Knee Instability
The knee may feel unstable or like it is "giving way," especially during activities that involve rapid pivoting or changes in direction.
Limited Range of Motion
The knee may feel stiff, and it may be difficult to bend or straighten the leg completely.
Difficulty Walking
Walking, particularly on uneven surfaces or downhill, may become difficult due to pain or instability in the knee.
Tenderness
The area around the back of the knee may be tender to the touch, particularly if there is inflammation or swelling.
Popping or Clicking Sensation
A feeling of popping or clicking may occur at the time of injury, particularly in cases of significant ligament damage.
Bruising
In severe cases, bruising may appear around the knee due to internal bleeding from the torn ligament or surrounding tissues.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Expert Specialists for PCL Injuries
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

High-Impact Sports
Athletes who engage in sports that involve rapid deceleration, direction changes, or contact (e.g., football, soccer, basketball) are at higher risk of PCL injuries.

Direct Trauma or Impact
A common cause of PCL injuries is a direct blow to the knee, such as when the knee hits the dashboard in a car accident or during a tackle in sports.

Hyperextension of the Knee
PCL injuries often occur when the knee is forcefully bent backward, such as during a sudden fall or misstep.

Previous Knee Injuries
Individuals who have previously injured the knee, particularly those with ACL or MCL (medial collateral ligament) injuries, are more likely to sustain a PCL injury due to altered knee mechanics or muscle weakness.

Weak Muscles Around the Knee
Weakness in the quadriceps and hamstrings can place additional strain on the ligaments, increasing the risk of injury.

Age
Younger individuals, especially athletes, tend to be more susceptible to traumatic PCL injuries. As we age, the ligaments lose elasticity and can become more prone to sprains and tears.

Obesity
Excess body weight places additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of ligament injuries, including PCL tears.

Poor Footwear
Wearing improper or unsupportive footwear during physical activity can lead to poor alignment and increase the chances of knee injury.

PCL Injuries
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
- Protein: Protein is essential for repairing tissues, including ligaments and muscles. Lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes provide the necessary amino acids for tissue regeneration.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C helps with collagen production, an essential component of ligaments. Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are rich sources of Vitamin C and can aid in the recovery process.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce pain and swelling associated with PCL injuries. Fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds are excellent sources.
- Vitamin D and Calcium: These nutrients are vital for bone health, which supports the knee joint. Ensure adequate intake through dairy products, leafy greens, and sunlight exposure.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These compounds are essential for joint health and may help protect ligaments and cartilage. They are commonly found in supplements and some joint health foods.
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in muscle relaxation and tissue repair. Foods like spinach, almonds, and whole grains are rich in magnesium.
- Zinc: Zinc supports immune function and tissue repair, which can speed up recovery after ligament injuries. Pumpkin seeds, cashews, and lentils are high in zinc.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining joint health and ensuring that the synovial fluid in the knee joint works properly to lubricate the ligaments and cartilage.
- Turmeric and Ginger: Both have powerful anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce swelling and pain in the knee, promoting a faster recovery.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, can help provide better support for the PCL and reduce the risk of injury.
- Proper Technique: In sports like football and basketball, using proper techniques for deceleration, jumping, and pivoting can help reduce the strain on the knee ligaments.
- Warm-Up and Stretching: A proper warm-up and stretching routine before physical activity can prepare the muscles and joints for movement, helping to prevent injuries.
- Use Proper Footwear: Wear appropriate shoes with proper arch support and cushioning for your specific activity. This helps maintain proper alignment and reduces strain on the knee.
- Avoid Overuse: Resting the knee and avoiding repetitive high-impact activities can reduce the risk of overloading the PCL and prevent injuries from overuse.
- Protective Equipment: In contact sports, wearing knee braces or sleeves can provide additional support and reduce the risk of PCL injuries during physical contact.
- Avoid Hyperextension: Be mindful of your knee’s range of motion, and avoid hyperextending the knee (forcing it backward) during activities to reduce stress on the PCL.
- Balance and Coordination Training: Exercises that improve balance and coordination can help prevent falls and improper movements that may lead to PCL injuries.
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess the knee for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. Special tests, such as the posterior drawer test or the Godfrey’s test, may be performed to check for PCL instability.
- X-rays: X-rays are used to rule out fractures or other bone issues, but they do not show soft tissue damage like ligament tears.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI is the gold standard for diagnosing soft tissue injuries like PCL tears. It provides detailed images of the ligament and surrounding tissues, helping to assess the severity of the injury.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): A CT scan may be used in complex cases or when the MRI does not provide clear information. It helps visualize bone and ligament structures in more detail.
- Ultrasound: In some cases, an ultrasound may be used to evaluate soft tissue damage and check for tears or inflammation in the PCL.
- Pain Management: The first line of treatment is often pain management, which can include rest, ice therapy, elevation, and medications such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Physical Therapy: Once the pain is controlled, physical therapy is crucial to restore strength, flexibility, and stability to the knee. Exercises will focus on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles to support the PCL.
- Bracing: In some cases, a knee brace may be recommended to help stabilize the knee joint during recovery.
- Surgical Treatment: In more severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the torn PCL. Surgical options include PCL reconstruction, which involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft.
- Regenerative Medicine: Treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or stem cell injections may be used to promote healing and reduce inflammation in the knee.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: After surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is essential for restoring knee function and preventing future injuries. This typically involves a combination of strength-building exercises, stretching, and gradual return to activity.
- Orthopedic Clinics: Specialized clinics that focus on musculoskeletal conditions, including knee injuries. These clinics provide both conservative and surgical treatments for PCL injuries.
- Sports Medicine Centers: Clinics that specialize in treating sports-related injuries, including PCL tears. They offer rehabilitation services, pain management, and advanced treatments like PRP therapy.
- Physical Therapy Clinics: Rehabilitation centers that provide physical therapy to restore mobility and strength to the knee after a PCL injury.
- Diagnostic Imaging Centers: Hospitals or clinics with MRI, CT, and ultrasound capabilities to accurately diagnose PCL tears and assess the extent of the injury.
Surgical Centers: Centers equipped to perform minimally invasive knee surgeries, such as PCL reconstruction, to repair the damaged ligament.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your PCL Injury Recovery Journey?
Learn More About PCL Injury Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Recovery time depends on the severity of the injury. Minor injuries may take 6-8 weeks, while more severe cases requiring surgery can take 6-12 months for full recovery, including rehabilitation.
Mild PCL injuries may heal with rest, physical therapy, and other conservative treatments. However, severe PCL tears may require surgical intervention for complete recovery.
Treatment for a PCL injury may include rest, ice, physical therapy, knee bracing, or surgery. Conservative treatments are often effective for mild injuries, while surgery may be required for severe tears.
