Advanced Spinal Fusion Surgery for Long-Lasting Back Pain Relief
Spinal Fusion stabilizes the spine, relieves chronic pain, and restores mobility using advanced surgical techniques.
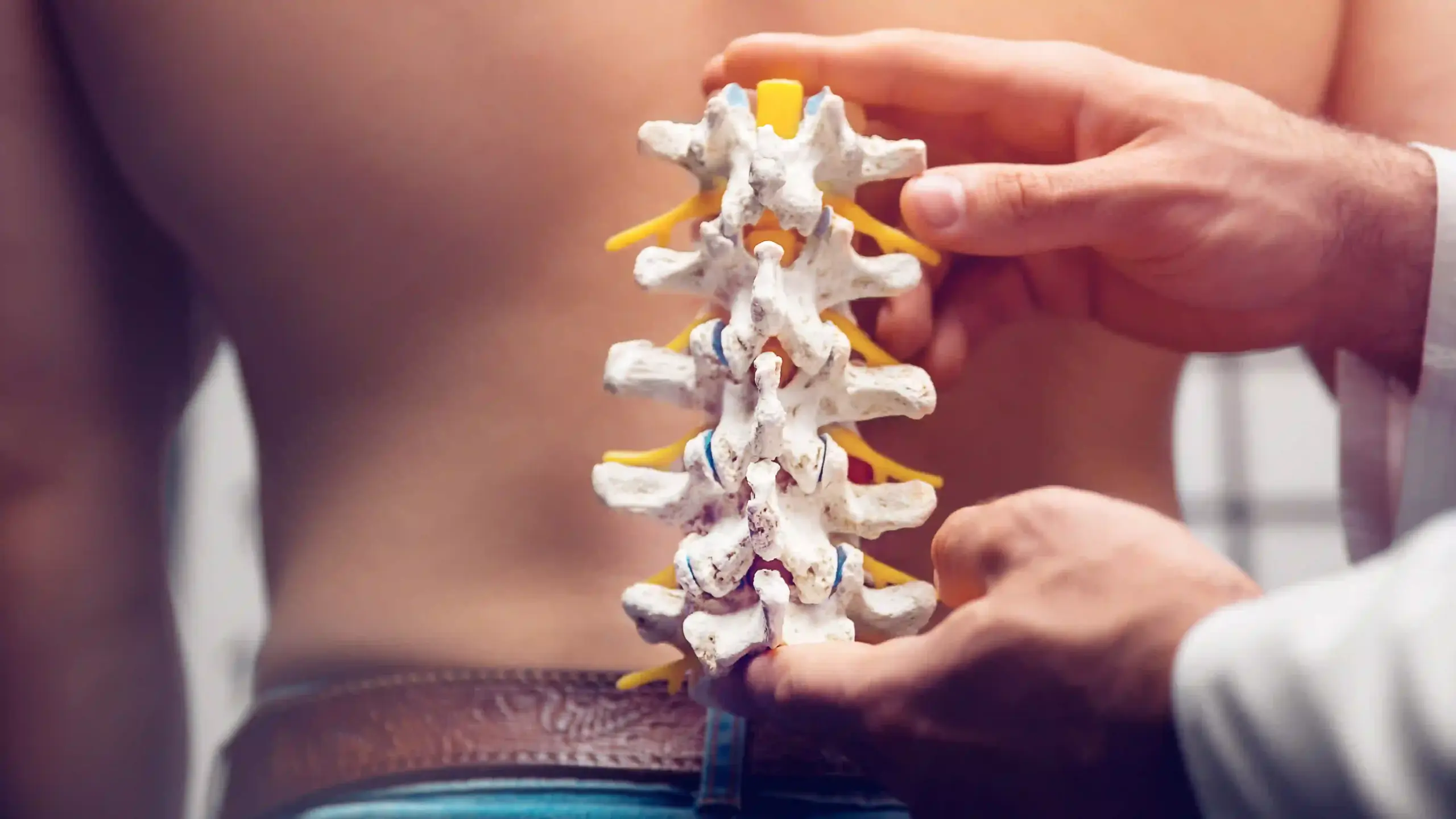
Spinal Fusion
Spinal Fusion is a surgical procedure that permanently joins two or more vertebrae in the spine to eliminate movement between them. It’s performed to stabilize the spine, reduce pain, and correct deformities caused by conditions like degenerative disc disease, scoliosis, fractures, or spinal instability. By fusing vertebrae using bone grafts, screws, or rods, it restores spinal alignment and prevents abnormal motion. The surgery significantly improves posture, mobility, and quality of life. Spinal Fusion is often recommended when non-surgical treatments fail to relieve chronic back pain or nerve compression, ensuring long-term stability and structural support for the spine.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Chronic Back Pain
Persistent pain that worsens with movement or posture changes.
Nerve Pain
Radiating pain down the legs (sciatica) or arms due to nerve root compression.
Limited Mobility
Difficulty bending, twisting, or walking due to spinal instability.
Deformity
Visible spinal curvature caused by scoliosis or vertebral slippage.
Muscle Weakness
Reduced strength in the lower limbs from compressed spinal nerves.
Numbness or Tingling
Loss of sensation in the extremities indicating nerve irritation.
Postural Imbalance
Trouble maintaining an upright posture due to spinal misalignment.
Loss of Function
In severe cases, patients may struggle with daily activities or balance.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Expert Spinal Fusion
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Degenerative Disc Disease
Aging and wear lead to disc collapse and instability.

Traumatic Injury
Accidents or falls can fracture or dislocate vertebrae.
Scoliosis or Kyphosis
Abnormal spinal curvature requiring corrective fusion.
Osteoarthritis
Deterioration of joints increases spinal instability.

Infections or Tumors
Can weaken vertebrae, necessitating surgical stabilization.

Obesity
Adds excess stress on the spine, accelerating degeneration.

Smoking
Reduces bone healing capacity after surgery.

Previous Spine Surgery
Increases the likelihood of requiring fusion for stability.

Genetic Factors
Inherited spinal deformities can predispose individuals to instability.

Spinal Fusion
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
A strong, well-nourished body promotes faster healing after spinal fusion surgery.
- Protein-Rich Foods: Aid in muscle and tissue repair; include eggs, fish, chicken, and lentils.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Strengthen bones and promote graft fusion; found in milk, cheese, and sunlight exposure.
- Magnesium: Helps with muscle relaxation and bone health; sources include nuts, spinach, and avocados.
- Vitamin C: Supports collagen formation for bone and tissue regeneration.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce inflammation; available in salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Hydration: Keeps joints and discs lubricated and supports overall recovery.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Both slow down bone healing and calcium absorption.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce sugar and trans fats to prevent inflammation and delay healing.
Although spinal fusion addresses existing problems, preventive care can protect against spine issues:
- Maintain Proper Posture: Keep your back straight when sitting or standing to prevent spinal strain.
- Regular Exercise: Strengthen back, abdominal, and core muscles to support spinal alignment.
- Healthy Weight Management: Excess body weight increases spinal pressure and disc wear.
- Quit Smoking: Enhances bone health and reduces risk of post-surgical complications.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium for strong bones.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Use correct lifting techniques to prevent disc injury or strain.
- Ergonomic Setup: Use supportive chairs, proper desk height, and avoid slouching.
- Routine Spine Check-ups: Detect early signs of degeneration or deformity for timely treatment.
Accurate diagnosis is vital to determine if spinal fusion is the right treatment option.
- Medical History Review: Identifies previous spine injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions.
- Physical Examination: Evaluates posture, muscle strength, and pain location.
- X-rays: Show spinal alignment and vertebral damage.
- MRI Scan: Reveals soft tissue issues such as herniated discs or nerve compression.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed 3D imaging for surgical planning.
- Bone Density Test: Assesses bone quality to ensure successful fusion.
- Electromyography (EMG): Tests nerve function and identifies compression severity.
- Diagnostic Injections: Pain relief injections help confirm the exact pain source before surgery.
Hospitals like VS Hospitals provide comprehensive spine care and advanced spinal fusion services using modern technology and a multidisciplinary approach.
- Minimally Invasive Fusion Surgery: Smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery compared to traditional methods.
- Robotic and Navigation-Assisted Surgery: Enhances surgical accuracy and precision in implant placement.
- Bone Grafting Techniques: Use of autografts (patient’s bone), allografts (donor bone), or synthetic materials for fusion.
- Scoliosis and Deformity Correction: Aligns and stabilizes spinal curvature in both adults and children.
- Spinal Instrumentation: Titanium rods, plates, and screws ensure permanent stability.
- Comprehensive Pain Management: Includes medications, nerve blocks, and physical therapy.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Tailored physiotherapy sessions for faster recovery and mobility restoration.
- Post-Surgical Monitoring: Continuous follow-ups to assess bone fusion progress via imaging tests.
- Patient Education: Guidance on movement restrictions, posture correction, and long-term spine care.
- Dedicated Spine Surgery Suites: Equipped with real-time imaging and advanced surgical navigation systems.
- Robotic Spine Centers: Provide precision-guided surgery with minimal complications.
- 3D Imaging and Intraoperative CT: Allows surgeons to visualize the spine in detail during surgery.
- Advanced Recovery Rooms: Designed for patient comfort and close post-operative monitoring.
- Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy Units: Offer personalized strength training and flexibility programs.
- Pain Management Clinics: Focused on non-opioid pain control and faster recovery.
- Bone Bank and Graft Preparation Labs: Provide high-quality bone materials for fusion.
- 24/7 Emergency and Trauma Unit: Handles spine fractures, slips, and acute nerve compression cases.
- Nutritional and Psychological Support: Promotes holistic healing and better post-surgical outcomes.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Spinal Fusion Journey?
Learn More About Spinal Fusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Spinal fusion has a success rate of around 85–95%, depending on the condition and patient health. It effectively stabilizes the spine and relieves chronic pain caused by fractures, degeneration, or deformities. Post-surgery rehabilitation and healthy lifestyle practices further improve recovery outcomes and spinal strength over time.
Recovery varies from person to person but generally takes 3–6 months for the bones to fuse completely. Most patients return to light work within 6–8 weeks. Physical therapy and a nutrient-rich diet significantly speed up recovery and prevent stiffness or complications after surgery.
Spinal fusion reduces movement in the fused segment, but it usually doesn’t affect overall flexibility or function. Patients often feel more stable and experience less pain after surgery. Maintaining good posture, core strength, and regular physiotherapy ensures a near-normal range of motion in daily life.
