Advanced Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Surgery for Better Joint Function
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty restores shoulder movement, reduces pain, and improves joint stability through advanced surgical precision and expert care.
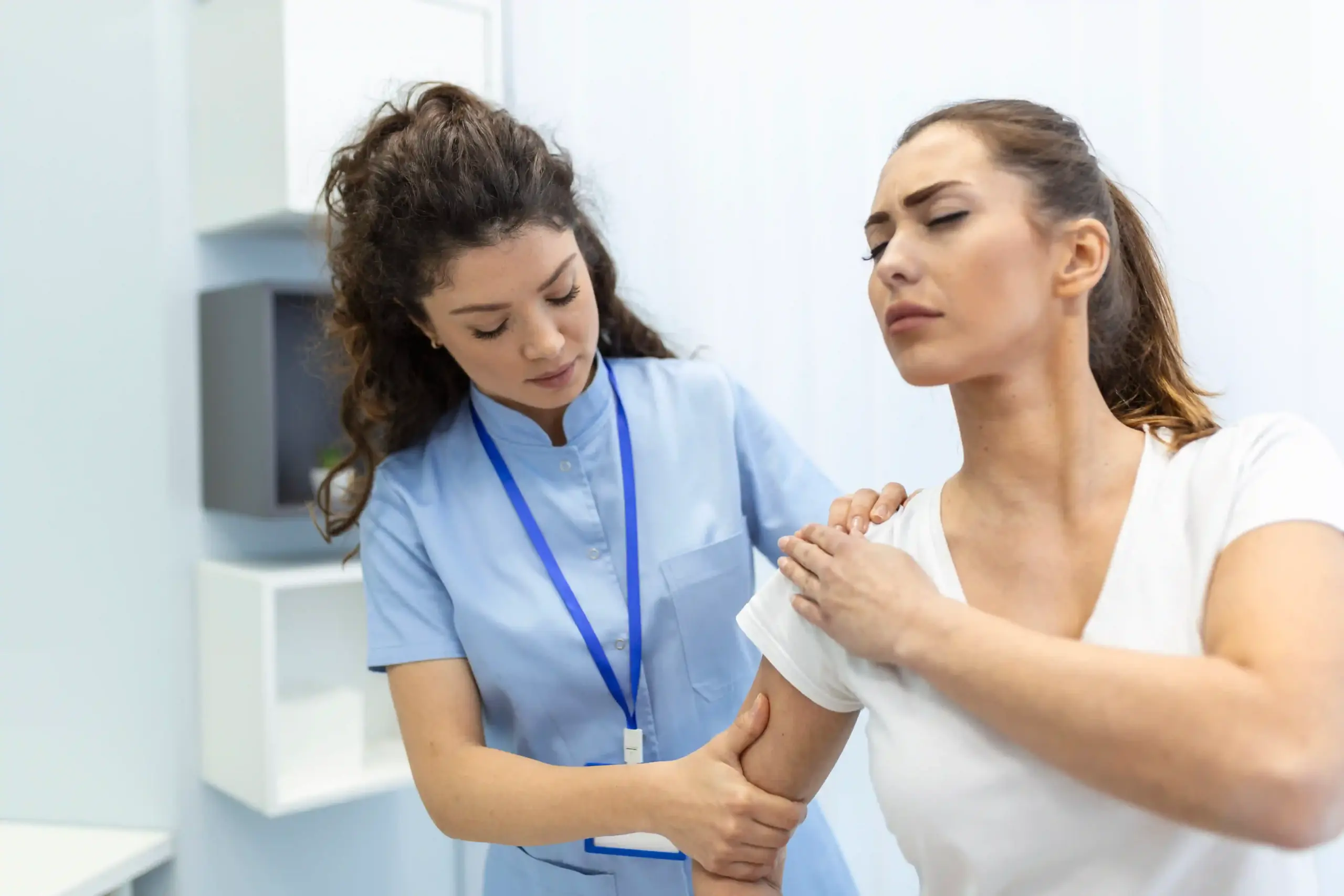

Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty (RSA) is a specialized type of shoulder replacement surgery that is often recommended for patients with severe shoulder arthritis, rotator cuff tears, or other joint diseases that cannot be effectively treated with traditional shoulder replacement. Unlike conventional shoulder replacement, where the ball and socket of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial components, RSA reverses the position of the ball and socket. In this procedure, the ball is attached to the shoulder blade (scapula), and the socket is placed at the top of the arm bone (humerus).
This reversal of the typical anatomy of the shoulder joint allows patients who have damaged or torn rotator cuffs to achieve improved function and mobility. RSA is primarily used in patients with rotator cuff arthropathy (a condition caused by a torn and arthritic rotator cuff) or patients who have failed other forms of shoulder surgery.
RSA is especially beneficial for patients who have arthritis and cannot rely on the rotator cuff muscles for normal shoulder movement. The surgery allows the deltoid muscle to take over the function of the damaged rotator cuff, making it possible to restore shoulder function and alleviate pain.

Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Severe Shoulder Pain
Chronic pain that does not improve with medication, physical therapy, or rest. The pain often worsens with overhead activities or when trying to lift the arm.
Limited Range of Motion
Difficulty in raising the arm or moving it across the body. Patients often feel "stuck" or unable to move the shoulder in any direction.
Weakness
Weakness in the shoulder due to rotator cuff damage or arthritis. This can limit the ability to perform everyday activities, such as reaching, dressing, or lifting.
Joint Stiffness
The shoulder feels stiff, and the patient may experience limited movement in all directions.
Deformity or Instability
In advanced cases, the shoulder may appear deformed or unstable due to the wear and tear of the joint or torn rotator cuff muscles.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Expert Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Age
RSA is typically recommended for patients over the age of 60, as the likelihood of rotator cuff damage and arthritis increases with age.

Rotator Cuff Tear
Chronic tears in the rotator cuff muscles can lead to rotator cuff arthropathy, which may result in the need for RSA.

Severe Shoulder Arthritis
Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis in the shoulder joint can cause the cartilage to wear away, resulting in pain and loss of function.

Previous Shoulder Surgery
Patients who have had multiple failed shoulder surgeries, such as traditional shoulder replacement or rotator cuff repairs, may require RSA.
Trauma or Injury
Fractures or dislocations in the shoulder, especially when accompanied by rotator cuff tears, can necessitate RSA for joint restoration.

Poor Bone Health
Conditions like osteoporosis, where bones are weakened, can make traditional shoulder replacements less effective, and RSA may be a better option for joint stability.

Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
Proper nutrition is essential before and after Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty to support healing and joint health:
- Protein-Rich Foods: Protein plays a crucial role in tissue repair and muscle building, essential after surgery. Good sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: These nutrients are important for bone health. Calcium-rich foods such as dairy, leafy greens, and fortified cereals help maintain strong bones, while Vitamin D aids in calcium absorption.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce post-surgical swelling. Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Antioxidants, found in foods like berries, spinach, and tomatoes, can help reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint, supporting a quicker recovery.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated helps in the healing process by ensuring proper circulation and supporting joint lubrication.
- Iron and Zinc: Iron-rich foods (e.g., lean meats, spinach) and zinc (e.g., nuts, seeds) are important for immune function and tissue repair.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet also reduces stress on the shoulder joint, promoting optimal recovery.
Although not all risk factors are preventable, certain actions can reduce the risk of needing Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty or improve outcomes:
- Avoid Overuse Injuries: Repetitive overhead motions (such as lifting or throwing) can contribute to rotator cuff tears. Limiting these activities or using proper techniques can help prevent injury.
- Strengthen Shoulder Muscles: Performing strengthening exercises, particularly for the rotator cuff and deltoid muscles, can improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury.
- Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture while standing, sitting, or lifting can help protect the shoulder from strain and injury.
- Warm-Up Before Activity: Properly warming up before engaging in physical activity can reduce the risk of muscle and tendon injuries.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can impair circulation and slow down the healing process, making recovery from shoulder surgery more difficult.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on all joints, including the shoulders, helping to prevent conditions like arthritis.
A thorough evaluation is required to determine if Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty is the appropriate treatment:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess shoulder strength, range of motion, and pain levels. They may also test the stability of the shoulder joint.
- X-Rays: X-rays are crucial for evaluating the condition of the shoulder joint, including bone damage, joint space narrowing, and signs of arthritis.
- MRI or CT Scans: These advanced imaging techniques provide detailed information about the soft tissues, including the rotator cuff, and can help identify the extent of damage.
- Arthrogram: In some cases, an arthrogram (an X-ray procedure using dye to highlight the shoulder joint) is used to evaluate joint space and soft tissue integrity.
Based on the findings from these diagnostic tools, the doctor will decide if Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty is the best course of action.
Hospitals or clinics offering Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty provide various services to ensure patient comfort and success:
- Pre-Operative Consultation: A detailed consultation to assess medical history, diagnostic results, and develop a personalized surgical plan.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Advanced robotic technologies may be used to assist in precise placement of the prosthesis, ensuring better alignment and optimal outcomes.
- Pain Management: Comprehensive pain management techniques, including nerve blocks, medications, and post-surgical care to ensure comfort during recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Structured rehabilitation programs to restore strength, mobility, and function in the shoulder post-surgery. Physical therapy is vital for regaining a full range of motion.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process, check for complications, and ensure proper function of the implant.
Hospitals or clinics offering Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty should have specialized facilities to ensure safe and effective surgery and recovery:
- State-of-the-Art Surgical Theaters: Equipped with advanced imaging systems, robotic assistance, and surgical tools to perform the procedure with precision.
- Rehabilitation Centers: On-site physical therapy and rehabilitation services to help patients regain full use of their shoulder joint.
- Recovery Rooms: Comfortable rooms for patients to recover under close monitoring with nursing support to manage pain and complications.
- Orthopedic Departments: Specialized teams of orthopedic surgeons, nurses, and physical therapists focused on shoulder health and recovery.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: Dedicated care units to monitor patients for complications like infection, dislocation, or blood clots after surgery.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Journey?
Learn More About Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Recovery time can vary, but most patients can expect a period of 3 to 6 months to regain full mobility and strength. Initially, physical therapy is essential for restoring motion and improving strength, and regular follow-ups are necessary to monitor progress.
Like any surgery, Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty carries risks such as infection, blood clots, nerve damage, or prosthesis dislocation. However, these risks are minimized with proper surgical techniques, pre-operative care, and post-operative monitoring.
On average, the implant used in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty can last between 15 to 20 years, depending on factors like the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor the condition of the prosthesis.
