Expert Care for Bezoars and Foreign Bodies
Providing advanced diagnosis, safe removal, and specialized treatment for bezoars and foreign bodies at VS Hospitals.

Bezoars & Foreign Bodies
Bezoars and foreign bodies are conditions related to the accumulation or ingestion of indigestible materials in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. While foreign bodies are external objects accidentally or intentionally swallowed — such as coins, pins, buttons, or bones — bezoars are masses formed within the stomach or intestines from materials that the digestive system cannot break down, like hair, vegetable fibers, or medications.
At VS Hospitals, we provide specialized diagnosis and treatment for bezoars and foreign bodies with state-of-the-art endoscopic and minimally invasive techniques. Our team of expert gastroenterologists and surgeons ensures safe, precise, and effective management of these potentially dangerous conditions.

Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Abdominal Pain or Discomfort
Persistent or cramping abdominal pain, often in the upper region, is a common symptom, especially when the object causes partial or complete obstruction.
Nausea and Vomiting
Frequent vomiting may occur when food or fluids cannot pass through the digestive tract due to obstruction.
Loss of Appetite
Patients may experience reduced appetite or a sensation of fullness even after eating small portions, often caused by bezoars occupying space in the stomach.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
If the foreign body is lodged in the esophagus or upper digestive tract, it can cause pain or difficulty swallowing.
Bloating and Indigestion
Gas accumulation, bloating, and heartburn-like symptoms are common when the stomach cannot empty properly.
Constipation or Diarrhea
Depending on the location of the blockage, patients may experience altered bowel habits, either constipation due to obstruction or diarrhea from irritation.
Blood in Stool or Vomit
Sharp objects or bezoars can damage the intestinal lining, leading to bleeding, visible as dark stools or vomit containing blood.
Weight Loss
Long-term obstruction or indigestion can result in unintentional weight loss and nutritional deficiencies.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
If any of these symptoms persist, it is vital to seek immediate medical care at VS Hospitals for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
Meet Our Expert Bezoars & Foreign Bodies Specialists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Age
Children, especially those under five, frequently swallow small objects while playing. Elderly patients may also be at higher risk due to poor dentition or difficulty swallowing.
Psychiatric Conditions
Individuals with mental health disorders, such as pica, trichotillomania, or obsessive-compulsive behaviors, may ingest non-food materials like hair, paper, or stones.

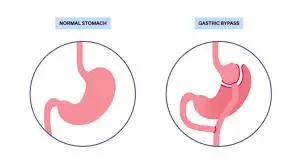
Previous Gastric Surgery
Surgeries such as gastric bypass or partial gastrectomy can alter the stomach’s motility, leading to bezoar formation.
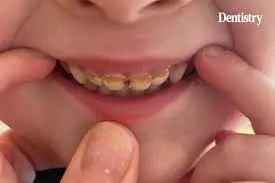
Poor Dental Health
Difficulty chewing food properly due to missing teeth or dentures can cause larger food particles to accumulate and form bezoars.
Chronic Diseases
Conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, or scleroderma that slow down stomach emptying (gastroparesis) can increase the risk of bezoar formation.

Use of Certain Medications
Some medications, like antacids, fiber supplements, or slow-dissolving tablets, can contribute to bezoar formation when not taken with sufficient water.

Dietary Habits
Diets high in fibrous foods, such as celery, pumpkin, or persimmons, can cause phytobezoars — the most common type of bezoar formed from plant material.

Alcohol or Drug Abuse
Intoxication or impaired coordination may increase the risk of accidental ingestion of foreign bodies.

Neurological Disorders
Patients with stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or dementia may experience swallowing difficulties (dysphagia), increasing the risk of foreign body ingestion.
Bezoars & Foreign Bodies
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
Proper diet management plays a vital role in preventing and recovering from bezoars and foreign body-related digestive issues. Nutrition experts at VS Hospitals customize diet plans to ensure smoother digestion and faster recovery.
- Soft, Well-Cooked Meals: Reduce the burden on the stomach and prevent undigested material from accumulating.
- High-Fiber Foods (in moderation): Include soluble fiber like oats, bananas, and apples to regulate digestion but avoid excessive insoluble fiber that may clump.
- Hydration: Drinking 2–3 liters of water daily supports gastric motility and reduces constipation risk.
- Avoid Indigestible Foods: Reduce intake of persimmons, celery, coconut, and pumpkin seeds — common causes of phytobezoars.
- Chew Thoroughly: Proper chewing prevents large food particles from forming bezoars.
- Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco: These habits delay digestion and irritate the gastric lining.
- Small, Frequent Meals: Improve digestion and prevent stomach overloading.
- Post-Surgery Diet Plans: Tailored low-residue diets are provided for patients with altered gastric anatomy.
The dietary guidance from VS Hospitals’ gastro dietitians ensures long-term digestive comfort and lowers the recurrence risk of bezoars.
Preventing bezoars and foreign body ingestion involves awareness, caution, and mindful eating practices. The gastroenterology team at VS Hospitals focuses on patient education and preventive lifestyle adjustments.
- Chew Food Slowly and Properly: Encourages complete digestion and prevents large food particles from forming masses.
- Supervise Children: Keep small items like coins, pins, and batteries out of children’s reach.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene and Dental Fit: Regular dental check-ups prevent accidental swallowing of dentures or crowns.
- Avoid Overuse of Antacids: Prolonged use can slow digestion and promote bezoar formation.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate fluid intake promotes smooth gastric movement.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: Patients who’ve undergone stomach or bariatric surgery should attend regular follow-ups at VS Hospitals.
- Be Cautious with Fiber Supplements: Excessive or unchewed fiber tablets can clump and form bezoars.
- Monitor Psychiatric or Behavioral Conditions: Psychological support helps reduce harmful ingestion habits.
At VS Hospitals, preventive gastro care is not just about treatment it’s about building lifelong digestive awareness.
Diagnosis of bezoars and foreign bodies involves a detailed medical history, clinical examination, and imaging studies to determine the object’s location, size, and impact. At VS Hospitals, a multidisciplinary approach ensures precise and safe diagnosis using advanced technologies.
- Clinical Evaluation: Initial assessment includes symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, and difficulty swallowing.
- Patient History: Review of dietary habits, prior surgeries, and psychiatric conditions helps identify risk factors.
- X-ray Imaging: Detects radiopaque objects like coins, bones, or metal pieces within the digestive tract.
- Ultrasound and CT Scan: Ultrasound locates non-metallic objects, while CT provides detailed obstruction imaging.
- Endoscopy: Offers direct visualization and enables simultaneous removal of the foreign body.
- Barium Swallow Test: Highlights gastrointestinal blockages or abnormalities through contrast X-ray imaging.
At VS Hospitals, our gastroenterology and surgical teams provide specialized treatment for patients with bezoars or foreign body ingestion. The focus is on minimally invasive, safe, and quick recovery-based interventions.
- Endoscopic Removal: The first-line and safest approach where a flexible endoscope is used to visualize and remove or fragment bezoars and foreign bodies.
- Chemical or Enzymatic Dissolution: Digestive enzymes or chemical agents like cellulase or papain help dissolve bezoars without surgery.
- Laparoscopic or Open Surgery: Performed when endoscopic methods fail; laparoscopy ensures minimal invasion and faster recovery, while open surgery is reserved for complex cases.
- Pediatric Management: Specialized pediatric gastroenterologists use gentle, safe techniques for children who swallow small objects.
- Psychiatric & Behavioral Support: Counseling and therapy are offered to patients with recurrent ingestion due to psychological causes.
- Nutritional & Post-Treatment Care: Dietitians guide patients on safe eating habits, and regular follow-ups prevent recurrence or complications.
The goal at VS Hospitals is to restore digestive function safely, relieve symptoms quickly, and prevent future occurrences.
VS Hospitals is one of Chennai’s leading multispecialty institutions, offering world-class infrastructure and technology to treat gastrointestinal and digestive disorders effectively.
- Advanced Diagnostic Imaging: Equipped with high-resolution CT, MRI, ultrasound, and digital X-ray systems for precise gastrointestinal visualization.
- State-of-the-Art Endoscopy Unit: Features HD video endoscopes and specialized pediatric scopes for safe diagnosis and removal procedures.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery Suites: Dedicated laparoscopic theaters ensure precision treatment, faster recovery, and minimal post-surgical discomfort.
- 24/7 Emergency & Intensive Care: Round-the-clock emergency and critical care units handle acute ingestion or obstruction cases promptly.
- Comprehensive Gastroenterology Department: A multidisciplinary team of gastroenterologists, endoscopists, and surgeons provides holistic digestive care.
- Rehabilitation & Patient-Centered Care: Nutrition and recovery centers, along with hygienic inpatient facilities, ensure safe recovery and long-term digestive health.
VS Hospitals is committed to providing a blend of advanced technology, experienced professionals, and holistic care that ensures complete recovery and peace of mind for every patient.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Bezoars & Foreign Bodies
Learn More About Bezoars & Foreign Bodies
Frequently Asked Questions
Bezoars are indigestible masses that accumulate in the stomach or intestines. At VS Hospitals, treatment includes endoscopic removal, chemical dissolution, or minimally invasive surgery depending on the bezoar type and size, ensuring a quick and safe recovery.
If not removed, a foreign body can cause serious complications like intestinal blockage, perforation, infection, or internal bleeding. VS Hospitals uses advanced imaging and endoscopic tools to ensure timely and safe removal before complications arise.
Yes. Prevention includes eating slowly, chewing food thoroughly, avoiding swallowing non-food items, maintaining good dental health, and managing psychological conditions like trichophagia or pica. Regular check-ups at VS Hospitals can help monitor and prevent recurrence.
