Emergency & Trauma Care | 24/7 Critical Care
Get 24/7 emergency & trauma care in Chennai with rapid stabilization, advanced life support, and expert critical care for life-threatening injuries.
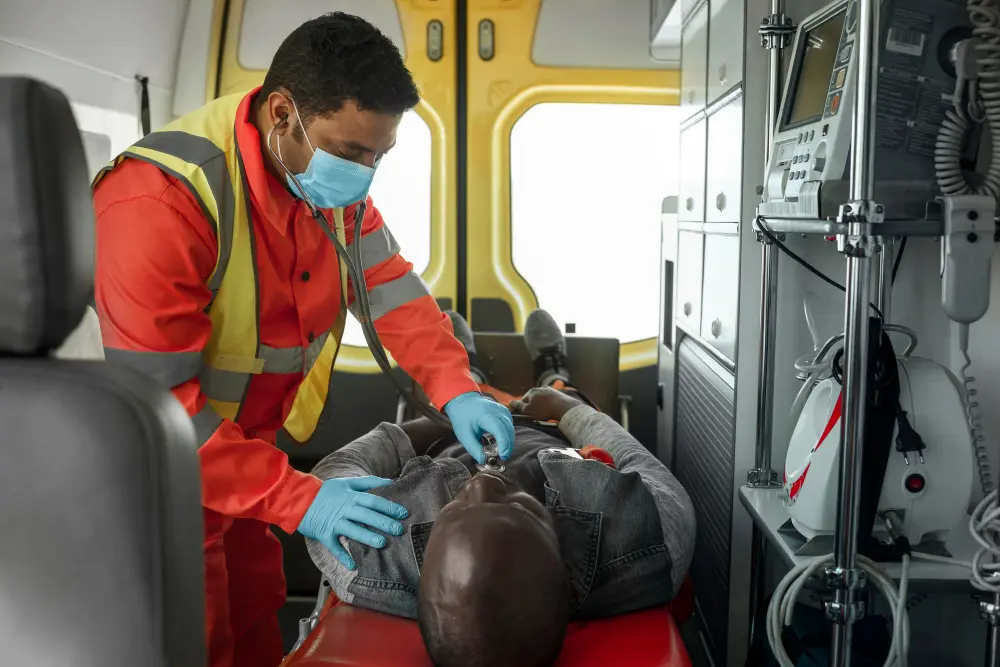

Emergency & Trauma
Emergency and trauma care deals with life-threatening injuries or medical conditions that demand immediate attention. These cases often involve accidents, severe bleeding, head injuries, cardiac arrest, burns, or fractures. The primary goal of emergency and trauma management is to stabilize the patient, prevent further damage, and provide life-saving interventions in the shortest possible time. Quick diagnosis, skilled response, and advanced medical infrastructure can make the difference between life and death.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Severe Pain or Bleeding
Uncontrolled bleeding, deep wounds, or visible fractures are red flags that require immediate medical attention.
Unconsciousness or Disorientation
Sudden loss of consciousness or confusion indicates brain injury or oxygen deprivation.
Breathing Difficulty
Shortness of breath, wheezing, or chest tightness could signal internal trauma, asthma, or cardiac events.
Abnormal Pulse or Blood Pressure
Rapid or very slow pulse may point to shock or internal bleeding.
Head and Neck Injuries
Severe headaches, vomiting, dizziness, or neck stiffness may suggest concussion or spinal injury.
Burns or Scalds
Redness, blistering, or charred skin can lead to infection or tissue damage if untreated.
Fractures and Dislocations
Visible bone deformities, swelling, or immobility are typical signs of skeletal trauma.
Abdominal Pain or Swelling
Could indicate internal bleeding, organ damage, or ruptured spleen/liver.
Seizures or Convulsions
Sudden jerky movements may stem from head injury, low oxygen, or neurological disorders.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Emergency & Trauma Care Specialists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Road Accidents
The most common cause of trauma cases, particularly in urban areas with heavy traffic.

Falls and Workplace Injuries
Construction sites, industrial zones, and elderly individuals are at high risk.

Sports Injuries
Contact sports or extreme activities can lead to head or spinal trauma.

Violence or Assault
Physical altercations and domestic violence contribute significantly to emergency trauma admissions.

Fire and Electrical Burns
Mishandling of electrical equipment or exposure to open flames increases injury risks.

Medical Emergencies
Heart attacks, strokes, allergic reactions, or seizures can occur without warning.

Natural Disasters
Earthquakes, floods, and building collapses can result in multiple trauma injuries.

Alcohol or Substance Abuse
Impairs coordination and increases the likelihood of accidents.

Neglected Safety Gear
Not using helmets, seat belts, or safety harnesses during risky activities enhances injury risk.

Emergency & Trauma
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
- Protein-Rich Foods: Essential for tissue repair and recovery. Include eggs, fish, chicken, legumes, and dairy.
- Vitamin C and Zinc: Accelerate wound healing and boost immunity. Citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds are key sources.
- Iron and Folic Acid: Crucial for blood regeneration after significant blood loss. Found in spinach, red meat, and beans.
- Hydration: Maintaining fluid balance helps prevent shock and supports organ function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce inflammation and promote nerve and brain recovery after trauma.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Blueberries, green tea, and leafy greens combat oxidative stress caused by trauma.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit sugar, caffeine, and alcohol during recovery to prevent delayed healing.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Strengthen bones, especially for patients recovering from fractures or joint injuries.
- Follow Road Safety Rules: Wear helmets, seat belts, and obey speed limits.
- Home Safety: Install anti-slip mats, secure loose wires, and keep sharp objects away from children.
- Occupational Safety: Use protective gear and follow industrial safety protocols strictly.
- Emergency Preparedness: Learn basic first aid, CPR, and have emergency contact numbers accessible.
- Fire Safety Measures: Keep fire extinguishers, avoid overloading sockets, and maintain electrical safety.
- Health Monitoring: Regular check-ups for hypertension, diabetes, or heart disease help prevent sudden emergencies.
- Mental Health Awareness: Address stress and emotional instability to prevent self-harm or impulsive behavior.
- Community Awareness Programs: Encourage participation in first-aid workshops and road safety drives.
- Primary Assessment (ABCDE): Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure are assessed first to stabilize vital functions.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs detect fractures, internal bleeding, or organ damage.
- Blood Tests: Check for infections, hemoglobin levels, and oxygen saturation.
- Ultrasound (FAST Scan): Rapidly identifies internal bleeding in the chest or abdomen.
- Neurological Examination: Determines brain injury severity using tools like the Glasgow Coma Scale.
- ECG and Cardiac Monitoring: Detects cardiac abnormalities or trauma-related arrhythmias.
- Pulse Oximetry: Monitors oxygen saturation in emergency care.
- Trauma Scoring Systems: Used by doctors to evaluate injury severity and predict survival outcomes.
- 24/7 Emergency Response: Immediate medical care for all life-threatening conditions, supported by ambulance services.
- Trauma Surgery: Includes management of fractures, internal injuries, and reconstructive operations.
- Critical Care Unit (ICU): Equipped with ventilators, defibrillators, and continuous monitoring systems.
- Burn Care Unit: Specialized facilities for severe burn management and skin grafting.
- Cardiac Emergency Services: For patients with chest pain, cardiac arrest, or arrhythmias.
- Neuro-Trauma Care: Manages brain and spinal injuries with neurosurgical support.
- Blood Bank Support: Ready availability of blood and plasma for transfusions.
- Poisoning & Toxicology Unit: Handles cases of drug overdose, food poisoning, or chemical exposure.
- Pediatric and Geriatric Emergency: Tailored care for age-specific trauma needs.
- Rehabilitation Services: Physiotherapy, counseling, and post-trauma recovery programs.
- Advanced Emergency Department: Well-equipped triage areas with high-tech monitoring equipment.
- Ambulance Network: GPS-enabled ambulances with paramedics trained in pre-hospital care.
- Operation Theatres: Dedicated trauma OTs with advanced surgical tools and sterile environments.
- ICU and HDU: Intensive and high-dependency units to manage critically ill patients.
- Diagnostics and Imaging: On-site X-ray, CT, MRI, and ultrasound for rapid diagnosis.
- Laboratory Support: 24-hour lab facilities for quick testing and blood analysis.
- Telemedicine and Emergency Coordination: Remote consultation with specialists for critical cases.
- Emergency Pharmacy: Round-the-clock access to essential drugs and life-saving medications.
- Post-Trauma Counseling: Psychological support to help patients recover emotionally.
- Multi-Disciplinary Team: Surgeons, anesthetists, cardiologists, neurologists, and physiotherapists working together for holistic care.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Breast Cancer Care Journey?
Learn More About Emergency & Trauma Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Stay calm, call for emergency help, and check the person’s breathing and pulse. If necessary, start CPR or control bleeding using pressure. Avoid moving the person if you suspect a spinal injury. Provide clear information to paramedics when they arrive to ensure fast and effective treatment.
Complications can be reduced with immediate medical response, accurate diagnosis, and proper rehabilitation. Early wound cleaning, fluid replacement, and infection prevention are vital. Timely surgical intervention, nutritional support, and follow-up care prevent long-term disability and promote faster recovery.
Go to an emergency room for severe chest pain, breathing difficulty, major bleeding, head injury, fractures, burns, or loss of consciousness. Clinics handle minor issues, but emergencies require hospitals with advanced facilities and trauma specialists for immediate intervention.
