Expert Diagnosis and Treatment for Thyroid Cancer
Get expert thyroid cancer diagnosis, personalized treatment, and advanced care from specialists at VS Hospitals.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of the neck and is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. Thyroid cancer is relatively rare compared to other cancers, but its incidence has been rising in recent years. The good news is that thyroid cancer is often treatable, especially when detected early. At VS Hospitals, we provide advanced and comprehensive care for thyroid cancer, from early diagnosis to specialized treatment options tailored to each patient’s needs.
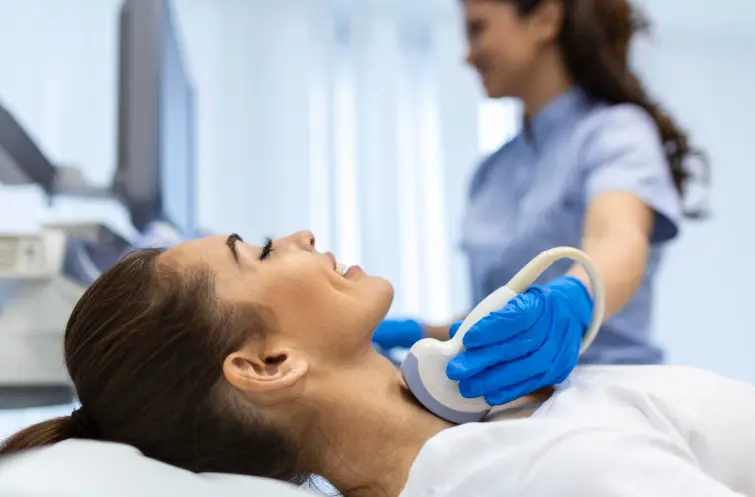
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
A Lump or Nodule in the Neck
A lump or swelling in the neck, which may be felt during a routine check-up or while swallowing, is one of the most common signs of thyroid cancer.
Changes in Voice
Hoarseness or voice changes that persist over time, particularly if they don’t improve, could indicate thyroid cancer affecting the vocal cords.
Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing
As the tumor grows, it can press against the throat or windpipe, leading to difficulties with swallowing or breathing.
Neck Pain
Pain or discomfort in the neck, throat, or ears, particularly if it persists for several weeks, can be a sign of thyroid cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying can be a symptom of thyroid cancer, especially when combined with other signs like fatigue.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes in the neck may become swollen if cancer has spread, often causing tenderness and pain.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other, less serious conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation.
Meet Our Expert Thyroid Cancer Oncologists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Gender
Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men, with women accounting for about three out of four cases.

Age
The risk of thyroid cancer increases with age, although certain types of thyroid cancer can affect younger individuals, especially those in their 30s or 40s.

Family History
A family history of thyroid cancer or certain genetic conditions increases the risk of developing thyroid cancer. If someone in your immediate family has had thyroid cancer, your risk may be higher.

Genetic Mutations
Inherited conditions such as familial medullary thyroid cancer (FMTC) and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2) are linked to an increased risk of thyroid cancer.

Radiation Exposure
A history of exposure to high levels of radiation, particularly during childhood (such as radiation therapy for another condition), increases the risk of developing thyroid cancer.

Personal History of Thyroid Conditions
Conditions such as benign thyroid nodules or an enlarged thyroid (goiter) can increase the likelihood of thyroid cancer.

Dietary Deficiencies
A lack of iodine in the diet can increase the risk of thyroid cancer. Iodine is essential for proper thyroid function.

Thyroid Cancer
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
A healthy diet can support overall health and help reduce the risk of thyroid cancer. While no specific foods can prevent thyroid cancer, eating a well-balanced, nutritious diet can enhance immune function and support overall well-being, particularly during treatment. Here are some dietary recommendations:
- Increase Fruits and Vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants and essential nutrients, which help protect cells from damage and support thyroid function. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage are particularly beneficial.
- Consume Iodine-Rich Foods: Iodine is essential for proper thyroid function. Including iodine-rich foods like seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt in your diet can support thyroid health.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Limit Processed Foods: Highly processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined carbohydrates can contribute to inflammation and weight gain, which may negatively impact overall health. Opt for whole foods and avoid excessive sugar.
- Maintain Adequate Protein Intake: Protein is crucial for tissue repair and muscle health, particularly during and after cancer treatment. Include lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, legumes, and plant-based options.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain hydration, particularly if you are undergoing cancer treatments that may lead to dehydration or fatigue.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive alcohol consumption and caffeine can interfere with thyroid function and may exacerbate symptoms during treatment. Limiting these substances can support overall thyroid health.
Consulting with a registered dietitian who specializes in oncology can help create a personalized nutrition plan to ensure that you are getting the right nutrients while undergoing treatment.
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent thyroid cancer, certain lifestyle choices and health practices can reduce the risk:
- Limit Radiation Exposure: Avoid unnecessary exposure to radiation, especially in childhood. If you need radiation therapy for another condition, ask your doctor about ways to minimize the radiation dose to your thyroid.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and iodine, while avoiding processed foods, can help reduce the risk of thyroid cancer and promote overall health.
- Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular physical exams and check-ups can help detect any abnormalities in the thyroid early. If you have a family history of thyroid cancer or other thyroid conditions, discuss screening options with your healthcare provider.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can impact overall health and immune function. Practicing stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can support thyroid health.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for many types of cancer, including thyroid cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly lower your risk of developing thyroid cancer and improve your overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces inflammation, and supports overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can lower their risk of thyroid cancer and promote long-term health.
Early diagnosis is essential for the effective treatment of thyroid cancer. A variety of diagnostic tests are used to detect thyroid cancer, determine its type and stage, and plan appropriate treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Physical Exam: A healthcare provider will check for lumps or swelling in the neck and evaluate the thyroid for any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, including thyroid function tests, can help assess the thyroid’s health and detect any signs of abnormalities in hormone levels. A high or low level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) may indicate thyroid problems.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is commonly used to examine the thyroid gland and detect the presence of nodules or tumors. It can also help determine if a nodule is solid or cystic.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If a thyroid nodule is found, a fine needle aspiration biopsy may be performed to remove a small sample of tissue from the thyroid for testing. This is the most common method used to diagnose thyroid cancer.
- CT Scan or MRI: Imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs may be used to determine the size, location, and spread of thyroid tumors.
- Radioactive Iodine Scan: This scan is used to assess the function of the thyroid and to help identify whether thyroid cancer has spread to other areas.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic testing may be used to identify inherited conditions or gene mutations that increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
An accurate diagnosis helps determine the stage of thyroid cancer and guides the treatment approach.
VS Hospitals provides a wide range of services for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of thyroid cancer. These services include:
- Screening and Early Detection: Regular screenings for high-risk individuals, including blood tests and ultrasound exams, to detect thyroid cancer early.
- Surgical Oncology: VS Hospitals offers thyroidectomy (partial or total removal of the thyroid gland) for patients with thyroid cancer. Surgical procedures are performed using minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Radioactive iodine therapy is used to destroy remaining thyroid cancer cells after surgery, particularly for papillary or follicular thyroid cancers.
- Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Chemotherapy and targeted therapies may be used in advanced or aggressive cases of thyroid cancer, particularly for medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: After thyroid surgery, patients may need thyroid hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal metabolic function.
- Palliative Care: For patients with advanced thyroid cancer, palliative care is available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Rehabilitation and Support: VS Hospitals offers nutritional counseling, physical therapy, and psychological support to help patients manage the emotional and physical aspects of treatment.
VS Hospitals is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities to provide comprehensive care for thyroid cancer patients:
- Advanced Diagnostic Imaging: The hospital uses the latest technologies, including ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, for accurate diagnosis and staging of thyroid cancer.
- Surgical Suites: Modern, fully equipped surgical suites allow for minimally invasive and traditional thyroid surgeries, ensuring a faster recovery and minimal scarring.
- Radiation Therapy Units: VS Hospitals provides cutting-edge radiation therapy options, including radioactive iodine therapy, to target and destroy thyroid cancer cells.
- Oncology Department: The oncology department is staffed with experienced specialists in thyroid cancer, offering a multidisciplinary approach to treatment and care.
- Patient-Centered Care: VS Hospitals emphasizes holistic care, providing private rooms, nutritional support, counseling, and emotional care to ensure the well-being of each patient throughout their treatment journey.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Thyroid Cancer Care Journey?
Learn More About Thyroid Cancer Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Common symptoms of thyroid cancer include a lump or swelling in the neck, voice changes, difficulty swallowing, neck pain, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. If any of these symptoms persist, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
At VS Hospitals, thyroid cancer is treated with surgery (thyroidectomy), radioactive iodine therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies, depending on the type and stage of cancer. A personalized treatment plan is developed for each patient.
While thyroid cancer cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle changes, such as limiting radiation exposure and maintaining a healthy weight, can reduce the risk. Regular screenings for high-risk individuals and prompt treatment of thyroid conditions can also improve outcomes.
