Advanced Diagnosis and Treatment for Prostate Cancer
Advanced prostate cancer treatment by skilled oncologists for better outcomes.
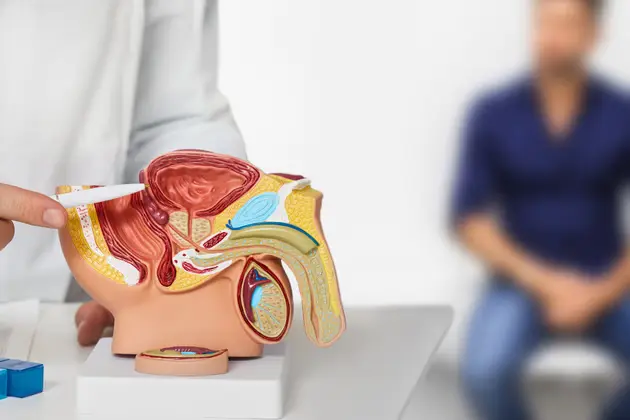
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men, particularly those over the age of 50. The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder, responsible for producing seminal fluid. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate begin to grow uncontrollably, potentially spreading to other areas of the body. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates, and advances in medical science have made it possible to manage prostate cancer effectively.
At VS Hospitals, a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach is used to diagnose and treat prostate cancer, ensuring that patients receive personalized care to achieve the best possible outcomes.
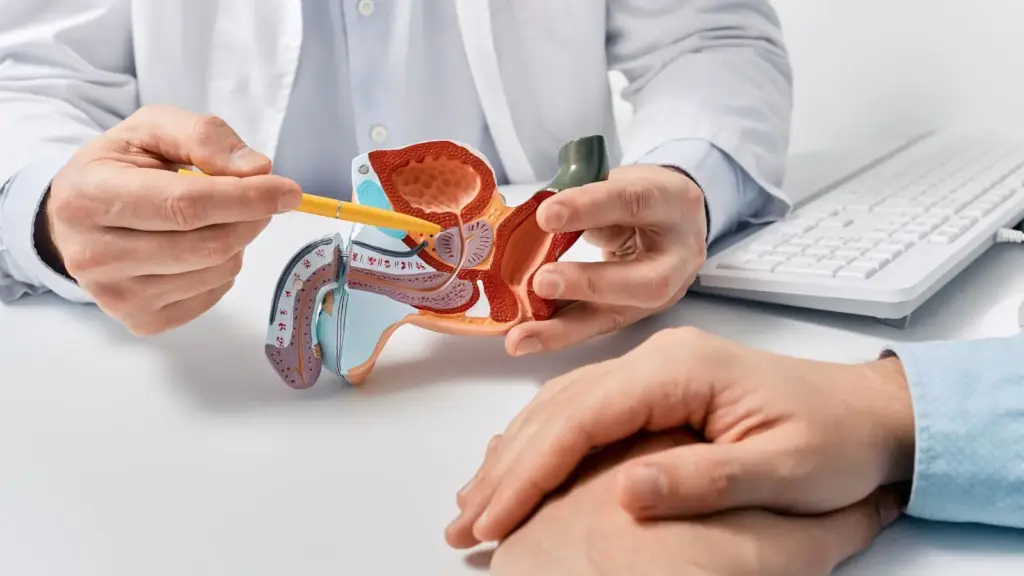
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Frequent Urination
Particularly at night (nocturia), a common sign of prostate problems, including prostate cancer.
Painful Urination
Difficulty or discomfort during urination, sometimes accompanied by a burning sensation.
Weak or Interrupted Urine Flow
Difficulty starting or stopping urination or a weak stream of urine.
Blood in Urine or Semen
The presence of blood in the urine or semen can be an alarming sign and requires immediate medical attention.
Pain in the Lower Back, Hips, or Pelvis
Advanced prostate cancer may cause pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis if the cancer has spread to bones.
Erectile Dysfunction
Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection can be a symptom of prostate cancer.
Painful Ejaculation
Pain or discomfort during ejaculation can sometimes occur with prostate cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss without a known cause may be a sign of advanced prostate cancer.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Expert Prostate Cancer Oncologists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Age
The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, particularly in men over the age of 50. The risk continues to rise as men age.

Family History
A family history of prostate cancer or other types of cancer may increase the risk. If a first-degree relative (father, brother) has had prostate cancer, the risk is higher.

Ethnicity
Prostate cancer is more common in African American men and is often diagnosed at a younger age and with more aggressive forms of the disease. Asian and Hispanic men have a lower risk.

Genetics
Certain inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of prostate cancer. Men with these genetic mutations may develop the disease earlier.

Dietary Factors
Diets high in saturated fats and red meat and low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Low levels of vitamin D are also linked to a higher risk.

Obesity
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of aggressive prostate cancer and may affect treatment outcomes.

Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, such as those used in farming or manufacturing, may increase the risk of prostate cancer.

Prostate Cancer
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
A healthy diet plays an important role in prostate cancer prevention and management. Although diet alone cannot prevent prostate cancer, certain foods can help reduce the risk and support the body during treatment. Here are some dietary tips:
- Eat Plenty of Fruits and Vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, especially those high in antioxidants like tomatoes, berries, and leafy greens, may help reduce cancer risk. Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower have shown protective effects.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, beans, and vegetables, support digestion and overall health. Some studies suggest that high fiber intake may lower prostate cancer risk.
- Healthy Fats: Replace saturated fats found in red meat and dairy products with healthier fats from sources like olive oil, avocado, and nuts. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Limit Red Meat and Processed Foods: Reducing the consumption of red meat and processed foods can lower the risk of prostate cancer. Processed meats such as bacon, sausages, and hot dogs may increase the risk.
- Soy and Legumes: Some studies suggest that soy and legumes, which are rich in plant-based compounds called phytoestrogens, may help protect against prostate cancer.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity has been linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the risk and improve overall health.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of several cancers, including prostate cancer. Limiting alcohol and caffeine intake can promote better overall health.
Consulting with a registered dietitian specializing in oncology can help create a balanced nutrition plan that supports overall health and helps manage side effects from prostate cancer treatment.
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Regular Screening: Early detection through screening can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. Men at higher risk, such as those with a family history of prostate cancer, should discuss screening options with their doctor.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for various cancers, including prostate cancer. Quitting smoking can lower your risk of developing prostate cancer and improve your overall health.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while avoiding processed foods and excess red meat, can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese is associated with a higher risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help lower this risk.
- Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Reducing exposure to harmful chemicals, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals, can help lower the risk of prostate cancer.
While lifestyle changes cannot guarantee the prevention of prostate cancer, adopting these healthy habits can help reduce the risk and improve overall well-being.
Diagnosing prostate cancer early is essential for effective treatment. Several tests are used to detect and confirm prostate cancer:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A healthcare provider may perform a DRE to feel for any abnormalities in the prostate, such as lumps or hard areas, that could indicate cancer.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: A blood test that measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated levels of PSA may indicate prostate cancer, although other conditions can also cause elevated PSA levels.
- Biopsy: If abnormal results from the DRE or PSA test suggest prostate cancer, a biopsy may be performed. A small sample of prostate tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS): This imaging test is often used to guide the biopsy needle during a prostate biopsy. It helps doctors visualize the prostate and surrounding tissues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans are used to obtain detailed images of the prostate, helping doctors assess the size, shape, and location of any tumors.
- Bone Scans: If prostate cancer is suspected to have spread to the bones, a bone scan may be performed to detect metastasis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans are used to detect whether prostate cancer has spread to other organs, such as the lymph nodes or lungs.
Accurate diagnosis using these methods helps determine the stage of the cancer and guide treatment decisions.
VS Hospitals offers comprehensive services for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of prostate cancer. Key services include:
- Prostate Cancer Screening: Routine screening for high-risk individuals, including PSA tests and digital rectal exams, to detect prostate cancer early.
- Surgical Oncology: VS Hospitals offers advanced surgical procedures, such as prostatectomy, to remove the prostate gland in cases of localized prostate cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: The hospital offers state-of-the-art radiation therapy, including external beam radiation and brachytherapy, to target and treat prostate cancer.
- Chemotherapy and Hormone Therapy: Chemotherapy and hormone therapy are available for advanced or metastatic prostate cancer. These treatments aim to shrink tumors and manage cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: VS Hospitals provides advanced treatments like immunotherapy and targeted therapy to treat aggressive or advanced prostate cancer.
- Palliative Care: For patients with advanced prostate cancer, palliative care services are offered to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life.
- Rehabilitation Services: The hospital provides post-treatment rehabilitation, including physiotherapy and counseling, to help patients recover and regain function after surgery or treatment.
VS Hospitals is equipped with modern facilities to ensure the best care for prostate cancer patients:
- State of the Art Diagnostic Equipment: The hospital uses advanced imaging technologies, including MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound, for accurate diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer.
- Oncology Department: The oncology department is staffed with experienced specialists who provide comprehensive care for prostate cancer patients, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- Surgical Suites: Fully equipped surgical suites allow for advanced prostate cancer surgeries, including robotic-assisted prostatectomy for minimally invasive treatment.
- Radiation Therapy Units: VS Hospitals offers cutting-edge radiation therapy options, ensuring precise targeting of tumors and minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Patient-Centered Care: The hospital provides private, comfortable rooms and a supportive environment to ensure that patients receive personalized care throughout their treatment journey.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Prostate Cancer Care Journey?
Learn More About Prostate Cancer Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Common symptoms of prostate cancer include frequent urination, painful urination, erectile dysfunction, blood in urine or semen, and pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis. However, many cases may not show symptoms until later stages, which is why regular screening is important.
At VS Hospitals, prostate cancer is treated using surgery (prostatectomy), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy. A personalized treatment plan is developed based on the type, stage, and aggressiveness of the cancer.
While prostate cancer cannot be entirely prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer. Regular screenings for high-risk individuals are also crucial for early detection.
