Early Detection and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer
Early detection, expert care, and advanced therapies for better recovery. Trust our multidisciplinary team for world-class Colorectal cancer treatment.
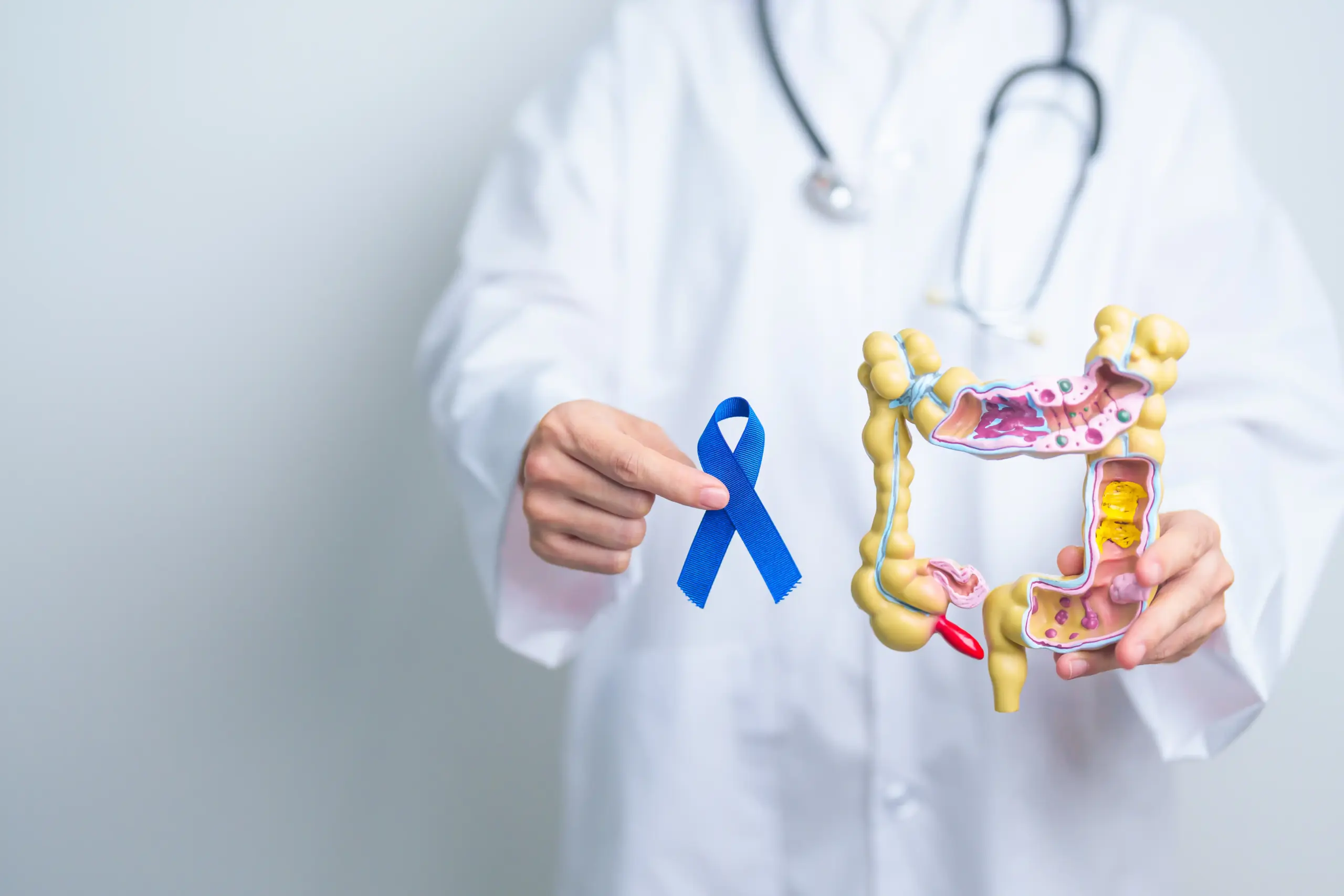
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the colon or rectum, parts of the large intestine. It is one of the most common cancers worldwide and affects both men and women. Colorectal cancer typically develops from polyps in the colon or rectum, which can grow into cancerous tumors over time. While it is most commonly diagnosed in older adults, it can occur at any age. Early detection through regular screenings and timely treatment are crucial to improving the chances of successful outcomes. At VS Hospitals, we offer comprehensive care for colorectal cancer, including advanced diagnostic tools, personalized treatment plans, and supportive services.

Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Changes in Bowel Habits
This includes diarrhea, constipation, or a feeling that the bowel is not emptying completely. These changes may persist over time and require attention.
Blood in Stool
One of the most common signs of colorectal cancer is blood in the stool. The blood may appear as bright red or darker, tarry stool.
Abdominal Pain or Cramping
Persistent or severe abdominal pain, bloating, or cramping can be associated with colorectal cancer, especially if accompanied by changes in bowel habits.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss without a known cause may be a sign of colorectal cancer.
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak, especially without a clear cause, is common in individuals with colorectal cancer.
Nausea and Vomiting
In advanced stages, the blockage of the colon can lead to nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
Rectal Bleeding
Bleeding from the rectum or blood in the stool can be an alarming symptom of colorectal cancer.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
If any of these symptoms persist for more than a few weeks or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical advice and undergo appropriate screening.
Meet Our Expert Colorectal Cancer Oncologists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Age
The risk of colorectal cancer increases significantly after the age of 50. However, younger adults can also develop colorectal cancer, particularly those with a family history or certain genetic conditions.
Family History
A family history of colorectal cancer or other types of cancer, particularly in close relatives, increases the risk of developing the disease.

Inflammatory Bowel Disease
People who have had colon polyps or inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis are at higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Genetic Conditions
Inherited conditions such as Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) significantly increase the risk of colorectal cancer.

Dietary Habits
A diet high in red or processed meats and low in fiber is linked to a higher risk of colorectal cancer. A low intake of fruits and vegetables can also increase the risk.

Obesity
Being overweight or obese is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer, particularly in those who have abdominal obesity.

Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of developing colorectal cancer. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves bowel function.

Smoking and Alcohol Use
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of colorectal cancer. These behaviors contribute to inflammation and the accumulation of harmful substances in the colon.

Colorectal Cancer
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
A healthy diet plays a vital role in reducing the risk of colorectal cancer and supporting overall health, particularly for individuals undergoing treatment. Below are some dietary recommendations for colorectal cancer prevention and management:
- Increase Fiber Intake: A diet rich in fiber, particularly from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, can help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber aids digestion and supports healthy bowel movements.
- Limit Red and Processed Meats: High consumption of red and processed meats, such as bacon, sausages, and hot dogs, is linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Opt for lean proteins like chicken, fish, and plant-based proteins.
- Eat Plenty of Fruits and Vegetables: A variety of fruits and vegetables, especially those rich in antioxidants like berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower), can help protect the colon from cancer.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and avocados, can reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
- Reduce Alcohol Intake: Limiting alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. Excessive alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing many cancers, including colorectal cancer.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of colorectal cancer, especially in those who are overweight or obese.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated is important for maintaining healthy bowel function and preventing constipation, a condition that can lead to complications in colorectal health.
- Avoid Sugar and Processed Foods: Limiting the intake of sugary foods and beverages, as well as processed foods, can reduce the risk of colorectal cancer by supporting a healthy weight and reducing inflammation.
A diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed and unhealthy options can support overall health and reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
While it is not possible to guarantee the prevention of colorectal cancer, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk:
- Regular Screening: Routine colorectal cancer screening, such as colonoscopies, is essential for detecting early signs of cancer, especially for individuals over the age of 50 or those with a family history. Early detection can lead to better outcomes and less aggressive treatment.
- Healthy Eating Habits: A diet high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, while low in red and processed meats, can help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves bowel function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for colorectal cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk and improve overall health.
- Limit Alcohol: Reducing alcohol consumption or avoiding it altogether can lower the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Managing conditions such as diabetes and obesity through diet, exercise, and medications can help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Genetic Counseling and Testing: If you have a family history of colorectal cancer or genetic conditions like Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis, genetic counseling and testing may help assess your risk and guide preventive strategies.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of colorectal cancer and improve their overall health.
The diagnosis of colorectal cancer involves several steps, including medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Colonoscopy: The most common and effective test for detecting colorectal cancer is a colonoscopy, where a long, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the colon to inspect for polyps, tumors, or abnormal growths. A biopsy can also be taken during this procedure for further examination.
- Blood Tests: A blood test, including the measurement of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level, can help assess overall health and detect signs of colorectal cancer, although it is not definitive for diagnosing cancer.
- Sigmoidoscopy: A sigmoidoscopy is similar to a colonoscopy but examines only the lower part of the colon (sigmoid colon). It may be used in some cases to detect abnormalities.
- CT Scan: A CT scan (computed tomography) is often used to assess the size and location of tumors and check for signs of metastasis (spread of cancer) to other organs.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of tissue from the colon or rectum to determine whether cancer cells are present. This is usually done during a colonoscopy.
- Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): This test detects hidden blood in the stool, which can be a sign of colorectal cancer. It is often used as a screening tool.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic testing may be used to identify inherited gene mutations that increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the stage of the cancer and developing the most effective treatment plan.
VS Hospitals provides a comprehensive range of services for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of colorectal cancer:
- Screening Programs: Regular screenings for early detection of colorectal cancer, including colonoscopies and fecal occult blood tests.
- Surgical Oncology: Expert surgeons perform minimally invasive and traditional surgeries, such as colon resections and tumor removals, to treat colorectal cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is available for patients with advanced colorectal cancer, aiming to shrink tumors and prevent cancer spread.
- Radiation Therapy: Advanced radiation therapy is offered to target and shrink colorectal tumors, particularly in cases where surgery is not possible.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: For advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer, targeted therapies and immunotherapy treatments are available to target specific cancer cells and boost the body’s immune response.
- Palliative Care: Palliative care services are available to manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and provide emotional support for patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
VS Hospitals is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities to provide the best care for colorectal cancer patients:
- Advanced Diagnostic Technology: The hospital uses cutting-edge diagnostic tools, including colonoscopy, CT scans, and MRI, to ensure accurate diagnosis and staging of colorectal cancer.
- Oncology Department: The oncology department at VS Hospitals specializes in colorectal cancer, offering multidisciplinary care and personalized treatment plans.
- Surgical Suites: Modern surgical suites equipped with the latest technology allow for minimally invasive procedures and accurate tumor removal.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Units: The hospital provides dedicated chemotherapy and radiation therapy units that are equipped with the latest technologies to ensure effective treatment.
- Supportive Care Services: VS Hospitals offers psychological counseling, nutritional support, and rehabilitation services to help patients during and after treatment.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Colorectal Cancer Care Journey?
Learn More About Colorectal Cancer Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Common symptoms of colorectal cancer include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. If any of these symptoms persist, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment for colorectal cancer at VS Hospitals includes surgery (colon resection), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. A personalized treatment plan is developed based on the cancer’s stage and location.
While colorectal cancer cannot be entirely prevented, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a fiber-rich diet, and avoiding smoking can help lower the risk. Regular screenings are crucial for early detection, especially for high-risk individuals.
