Comprehensive Care and Treatment for Liver Cancer
Get expert liver cancer treatment with advanced therapies, experienced specialists, and personalized care for improved recovery outcomes.
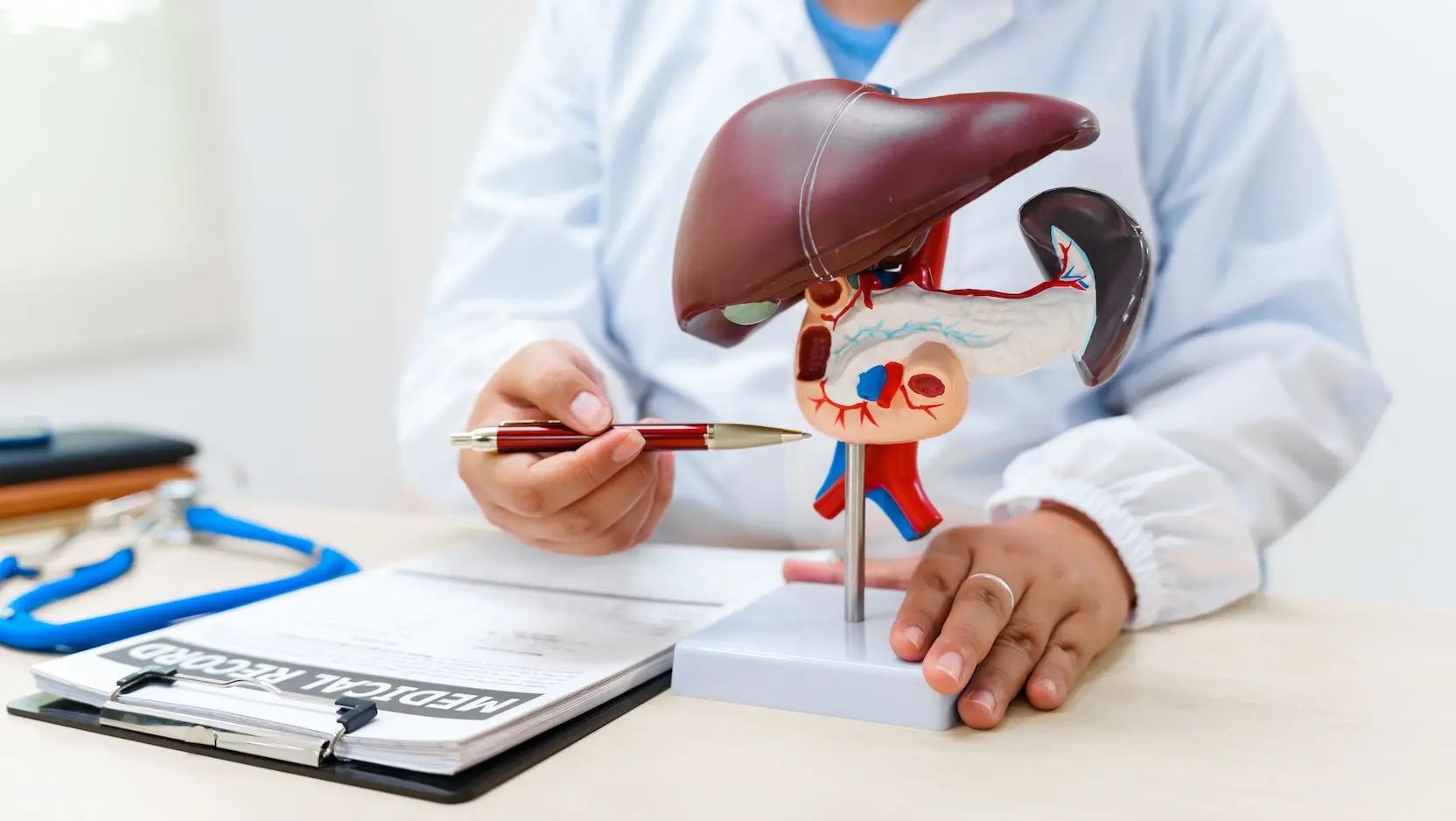
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer, or hepatic cancer, is a type of cancer that originates in the liver, one of the body’s most vital organs. The liver plays a key role in detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile, and storing energy in the form of glycogen. Liver cancer can either develop in the liver itself (primary liver cancer) or spread to the liver from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic liver cancer). Early detection and treatment are essential, as liver cancer often goes unnoticed in its early stages. At VS Hospitals, comprehensive care for liver cancer, from diagnosis to treatment, ensures the best possible outcomes for patients.
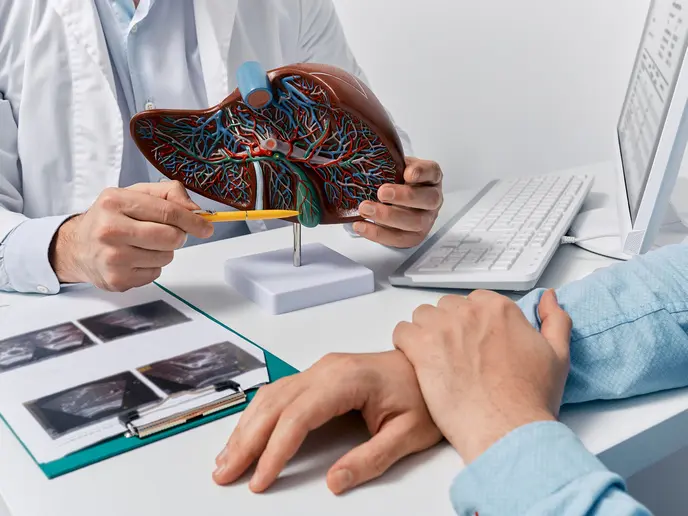
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the chances of survival. If you notice any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Signs and Symptoms
Unexplained Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying, especially in the presence of other symptoms, may indicate liver cancer.
Abdominal Pain or Swelling
Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen or unexplained swelling may be a sign that the liver is affected.
Loss of Appetite
A decrease in appetite and a feeling of fullness after eating only a small amount of food is common in individuals with liver cancer.
Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs when the liver is unable to process bilirubin, a waste product from red blood cells, effectively.
Nausea and Vomiting
Persistent nausea and vomiting, often with an accompanying loss of appetite, may be symptoms of liver cancer.
Fatigue
Extreme tiredness or weakness that doesn't improve with rest can be a common symptom of liver cancer.
Dark Urine and Pale Stools
Dark-colored urine and light-colored stools are signs of liver dysfunction, which may be linked to liver cancer.
Easy Bruising or Bleeding
Liver cancer can interfere with the liver’s ability to produce clotting proteins, leading to easy bruising or excessive bleeding.
Blood in Urine
Hematuria - pink, red, or dark urine, the most common symptom
Frequent Urination
Feeling the need to urinate frequently, even when bladder is not full
Painful Urination
Experiencing pain or burning sensation while urinating
Back or Pelvic Pain
Pain that occurs as the cancer grows and spreads
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant weight loss not related to diet or exercise
Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or weak without a clear cause
Meet Our Expert Liver Cancer Oncologists
Risk Factors
Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading causes of bladder cancer. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the bladder, increasing the risk.

Gender
Men are at a higher risk of developing bladder cancer than women.
Chronic Bladder Infections or Inflammation
Conditions such as bladder infections and long-term bladder inflammation can increase the risk.

Exposure to Chemicals
Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, especially those used in the dye industry, rubber production, and chemical manufacturing, increases the risk.

Chronic Liver Disease
Conditions such as cirrhosis (often caused by alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis) significantly increase the risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B and C
Long-term infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) increases the risk of liver cancer. These viruses can cause chronic liver inflammation that may eventually lead to cancer.

Alcohol Abuse
Heavy and prolonged alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for liver cancer, often leading to cirrhosis and liver damage.

Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome can lead to fat buildup in the liver, increasing the risk of developing liver cancer, particularly in individuals with cirrhosis.
Family History
A family history of liver cancer or chronic liver disease increases the likelihood of developing the disease.

Age and Gender
Liver cancer is more common in men than in women and is often diagnosed in people over 50 years old.

Exposure to Aflatoxins
Aflatoxins are toxins produced by molds that grow on improperly stored food, particularly grains and nuts. Long-term exposure to these toxins can increase the risk of liver cancer.

Tobacco Use
Smoking increases the risk of liver cancer, particularly in individuals with chronic liver conditions or hepatitis.

Liver Cancer
Diet and Nutrition
Prevention
Diagnosis
Key Services
Key Facilities
A healthy diet can help support the liver and overall health, especially for individuals diagnosed with liver cancer. Nutrition plays a vital role in managing the disease and improving treatment outcomes. Here are some dietary recommendations for liver cancer prevention and management:
- Increase Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, spinach, kale, and other fruits and vegetables, can help protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins and oxidative stress.
- Consume Lean Proteins: Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and legumes, are important for tissue repair and maintaining muscle mass, especially during treatment.
- Whole Grains and Fiber: Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat, as well as fiber-rich vegetables and legumes, support digestive health and help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Limit Saturated Fats: Avoid high-fat foods, particularly those rich in saturated fats, such as fatty meats, fried foods, and processed snacks. These can worsen liver function and contribute to fatty liver disease.
- Include Healthy Fats: Healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and nuts are beneficial for the liver and overall health.
- Drink Plenty of Water: Hydration is essential for liver health and overall well-being. Drinking water throughout the day can help flush toxins out of the body and support liver function.
- Limit Salt and Processed Foods: High salt intake can lead to fluid retention, which is problematic for individuals with liver disease. Processed foods that are high in sodium should be avoided.
- Control Sugar Intake: Excess sugar and refined carbs can lead to weight gain and worsen conditions like fatty liver disease, so it is important to limit sugary foods and drinks.
A balanced diet can help support the liver during treatment and reduce symptoms related to liver cancer. Consulting with a dietitian or nutritionist can help create a personalized nutrition plan to ensure proper nutrition during the treatment process.
Although it may not be possible to prevent liver cancer entirely, adopting certain lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk:
- Vaccination Against Hepatitis B: The hepatitis B vaccine can protect against chronic HBV infection, reducing the risk of liver cancer. It is particularly important for individuals at high risk, such as healthcare workers and people with multiple sexual partners.
- Screening for Hepatitis C: Individuals at risk of hepatitis C infection, such as those who have used intravenous drugs or received blood transfusions prior to 1992, should undergo screening. Early detection of chronic hepatitis C can help prevent liver damage and cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Limiting or eliminating alcohol intake is crucial for liver health. Chronic alcohol abuse is a leading cause of liver damage and cancer.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease increase the risk of liver cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can reduce this risk.
- Avoid Exposure to Toxins: Reducing exposure to harmful substances such as pesticides, industrial chemicals, and aflatoxins can help lower the risk of liver cancer.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Individuals at higher risk, such as those with chronic liver disease or a family history of liver cancer, should undergo regular screening and check-ups to catch potential issues early.
While these steps cannot guarantee prevention, they significantly reduce the risk of developing liver cancer and improve overall liver health.
Early diagnosis of liver cancer is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, such as liver function tests and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels, help assess liver function and detect signs of cancer. High levels of AFP can be an indication of liver cancer.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to visualize the liver and detect tumors or abnormalities.
- CT Scan or MRI: These imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the liver and surrounding organs, helping to identify tumors and assess their size and location.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a small sample of liver tissue to examine for cancer cells. This is typically done when imaging tests suggest the presence of cancer.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure in which a small camera is inserted into the abdomen to directly view the liver and obtain tissue samples.
- Angiography: This test involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels to highlight any blood flow to the tumor, which helps in planning treatment strategies like surgery or embolization.
Early detection through these diagnostic methods significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival.
VS Hospitals offers a wide range of services for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of liver cancer. These services include:
- Liver Cancer Screening: Regular screenings for high-risk individuals, including blood tests, ultrasound, and CT scans, for early detection of liver cancer.
- Surgical Oncology: Expert surgeons perform liver resections (removal of cancerous parts of the liver) and liver transplantation for patients with advanced liver cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is used to shrink or kill cancer cells in the liver and surrounding areas. It is often part of the treatment for advanced liver cancer.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: Advanced therapies that target specific cancer cells or boost the body’s immune system to fight the cancer are available for patients with advanced liver cancer.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): A minimally invasive procedure used to destroy liver tumors using heat generated by radio waves.
- Palliative Care: For patients with advanced liver cancer, palliative care is offered to manage pain and improve quality of life.
VS Hospitals is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities to provide the best care for liver cancer patients:
- Advanced Diagnostic Technology: The hospital uses the latest imaging technologies, including ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs, to accurately diagnose liver cancer and monitor its progression.
- Oncology Department: The oncology department is staffed with experienced specialists in liver cancer, offering a personalized treatment plan for each patient.
- Surgical Suites: Modern surgical suites allow for advanced liver cancer surgeries, including minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic liver resection.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy Units: VS Hospitals provides dedicated chemotherapy and radiation therapy units that are equipped with the latest technologies to ensure the best possible outcomes.
- Patient-Centered Care: The hospital offers private rooms, nutritional support, and psychological counseling to ensure patients’ emotional and physical well-being during treatment.
Top Medical Facilities at Our Multispeciality Hospital – Here’s What Makes Us Different!
Ready to Begin Your Liver Cancer Care Journey?
Learn More About Liver Cancer Care
Frequently Asked Questions
Symptoms of liver cancer include unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain or swelling, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, and pain during urination or intercourse. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Treatment options for liver cancer at VS Hospitals include surgery (liver resection or transplant), chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiofrequency ablation (RFA). A personalized treatment plan is developed based on the stage and type of cancer.
While liver cancer cannot always be prevented, lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing exposure to toxins can lower the risk. Regular screenings and vaccinations for hepatitis B and C are also crucial for high-risk individuals.
